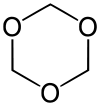
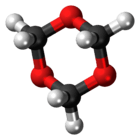
1,3,5-Trioxane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,3,5-Trioxane | |||
| Other names
s-Trioxane; 1,3,5-Trioxacyclohexane; Trioxymethylene; Metaformaldehyde; Trioxin | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 110-88-3 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:38043 | ||
| ChemSpider | 7790 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| RTECS number | YK0350000 | ||
| |||
| UNII | 46BNU65YNY | ||
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula |
C3H6O3 | ||
| Molar mass | 90.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 1.17 g/cm³ (65 °C)[1] | ||
| Melting point | 62 °C (144 °F; 335 K)[1] | ||
| Boiling point | 115 °C (239 °F; 388 K)[1] | ||
| 221 g/L[1] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| R-phrases | R22 | ||
| S-phrases | S24/25 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 45 °C (113 °F)[1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds |
Formaldehyde | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
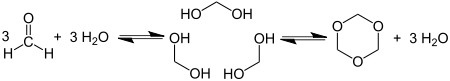
1,3,5-Trioxane, sometimes also called trioxane or trioxin, is a chemical compound with molecular formula C3H6O3. It is a white solid with a chloroform-like odor. It is a stable cyclic trimer of formaldehyde, and one of the three trioxane isomers; its molecular backbone consists of a six-membered ring with three carbon atoms alternating with three oxygen atoms. Thus, cyclotrimerization of formaldehyde affords 1,3,5-trioxane:
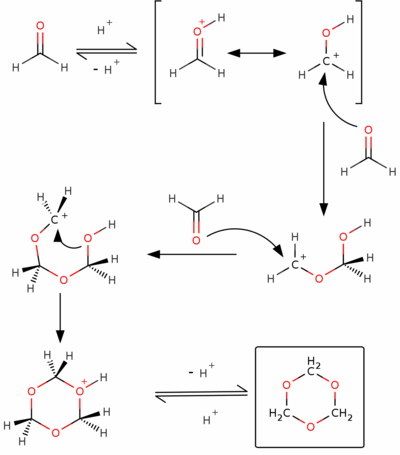
The mechanism can be explained in an acidic catalyzed reaction:
Uses
In chemistry, 1,3,5-trioxane is used as a stable, easily handled source of anhydrous formaldehyde. In acidic solutions, it decomposes to generate three molecules of formaldehyde. It may also be used in polymerization to form acetal resins, such as polyoxymethylene plastic. It is a feedstock for certain types of plastic, is an ingredient in some solid fuel tablet formulas, and is used in chemical laboratories as a stable source of formaldehyde.
Trioxane is combined with hexamine and compressed into solid bars to make hexamine fuel tablets, used by the military and outdoorsmen as a cooking fuel.
1,3,5-Trioxane is a mortician's restorative chemical that maintains the corpse's contours after postmortem tissue constriction.