1,2-Bis(dicyanomethylene)squarate
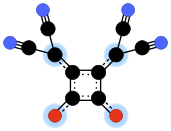
1,2-Bis(dicyanomethylene)squarate is a divalent anion with chemical formula C
10N
4O2−
2 or ((N≡C-)2C=)2(C4O2)2−. It is one of the pseudo-oxocarbon anions, as it can be described as a derivative of the squarate oxocarbon anion C
4O2−
4 through the replacement of two adjacent oxygen atoms by dicyanomethylene groups =C(-C≡N)2.
The anion can be obtained by reacting squaric acid with n-butanol to obtain the diester 1,2-dibutyl squarate (an oily orange liquid) and treating the latter with metallic sodium and malononitrile (N≡C-)2CH2 to give the trihydrated disodium salt 2Na+
·C
10N
4O2−
2·3H2O, a yellow water-soluble solid. The hydrated salt loses the water below 100 °C, but the resulting anhydrous salt is stable up to 400 °C.[1] Reaction of the sodium salt with the chlorides of other cations in ethanol affords the following salts:[1]
- dipotassium 2K+·K
2C
10N
4O2−
2, anhydrous, yellow, stable to 300 °C - dirubidium 2Rb+·Rb
2C
10N
4O2−
2, anhydrous, brown, stable to 300 °C - magnesium sodium chloride, Mg2+
·Na+·Cl−
·C
10N
4O2−
2·4.5H2O, dark yellow, dehydrates at 60–106 °C, stable to 461 °C - calcium disodium, 2Na+·Ca2+
·2C
10N
4O2−
2·9H2O, yellow, dehydrates at 50–90 °C, stable to 178 °C - barium, Ba2+
·C
10N
4O2−
2·2H2O, yellow, dehydrates at 87 °C, stable to 337 °C - tetra-n-butylammonium, 2(C
4H
5)4N+·C
10N
4O2−
2·H2O, yellow, dehydrates at 145 °C, stable to 323 °C
Nuclear magnetic resonance shows that the aromatic character of the squarate core is retained.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Vanessa E. de Oliveira, Gustavo S. de Carvalho, Maria I. Yoshida, Claudio L. Donnici, Nivaldo L. Speziali, Renata Diniz and Luiz Fernando C. de Oliveira (2009), Bis(dicyanomethylene)squarate squaraines in their 1,2- and 1,3-forms: Synthesis, crystal structure and spectroscopic study of compounds containing alkali metals and tetrabutylammonium ions. Journal of Molecular Structure Volume 936, Issues 1-3, Pages 239-249 doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2009.08.002