(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
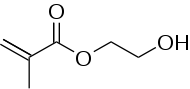
| IUPAC name
2-Hydroxyethyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
HEMA; Hydroxyethylmethacrylate; Glycol methacrylate; Glycol monomethacrylate; Hydroxyethyl methacrylate; Ethylene glycol methacrylate; 2-(Methacryloyloxy)ethanol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 868-77-9 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:34288 |
| ChemSpider | 12791 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image |
| KEGG | C14530 |
| |
| UNII | 6E1I4IV47V |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C6H10O3 |
| Molar mass | 130.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.07 |
| Melting point | −99 °C (−146 °F; 174 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 213 °C (415 °F; 486 K)[1] |
| Vapor pressure | 0.08 hPa |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | eye irritation |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Hydroxyethylmethacrylate or HEMA is the monomer that is used to make the polymer polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate. The polymer is hydrophobic; however, when the polymer is subjected to water it will swell due to the molecule's hydrophilic pendant group. Depending on the physical and chemical structure of the polymer, it is capable of absorbing from 10 to 600% water relative to the dry weight. Because of this property, it was one of the first materials to be successfully used in the manufacture of flexible contact lenses[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "GPS Safety Summary 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA)". July 2013.
- ↑ Blasco, Joe; Kehoe, Vincent J-R; The professional make-up artist : motion pictures, television, print, theatre; ISBN 0-9771580-0-4; LCC# PN2068.B53 2005