(341843) 2008 EV5
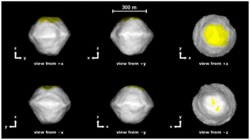
Principal axis views.[1]
(341843) 2008 EV5 (or 2008 EV5) is a near-Earth, potentially hazardous, Aten asteroid. It was discovered by the Mount Lemmon Survey in Tucson, Arizona, United States, on March 4, 2008.
2008 EV5 is an oblate spheroid 400 m (1,300 ft) in diameter. It rotates in a retrograde direction.[1] There is a 150 m (490 ft) diameter concave feature, possibly an impact crater, or a relict feature from a previous episode of rapid rotation that caused the asteorid's shape to reconfigure.[1] Visible and near-infrared spectroscopy show that 2008 EV5's composition is similar to that of carbonaceous chondrite meteorites.[2] 2008 EV5 is listed in the JPL Small-Body Database and classified as: Aten NEO, PHA (SPK-ID: 2341843).[3]
2008 EV5 is the preliminary baseline target of a sample-return NASA mission.[4][5] Besides the asteroid 2008 EV5, several other space rocks, including Itokawa and Bennu, are being considered for this mission.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Busch, Michael W. et al. (October 6, 2011). "Radar Observations and the Shape Near-Earth Asteroid 2008 EV5". NASA. Retrieved March 26, 2015.
- ↑ Reddy, Vishnu; Le Corre, Lucille; Hicks, Michale; Lawrence, Kenneth; Buratti, Bonnie; Abell, Paul; Gaffey, Michael; Hardersen, Paul (September 6, 2012). "Composition of Near-Earth Asteroid 2008 EV5: Potential target for Robotic and Human Exploration". arXiv. arXiv:1209.1207. Retrieved March 27, 2015.
- ↑ Staff (November 8, 2012). "JPL Small-Body Database Browser - 341843 (2008 EV5)". NASA. Retrieved March 26, 2015.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Steitz, David E. (March 25, 2015). "RELEASE 15-050 - NASA Announces Next Steps on Journey to Mars: Progress on Asteroid Initiative". NASA. Retrieved March 26, 2015.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Borenstein, Seth (March 25, 2015). "NASA details plans to pluck rock off asteroid, explore it". AP News. Retrieved March 26, 2015.
External links
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (340001)-(345000) (IAU Minor Planet Center)
| ||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||