Microsoft .NET Gadgeteer [1] is an Open Source rapid prototyping platform with an emphasis on creating small electronic or embedded hardware devices.[2] It brings the concept of software encapsulation to hardware components, enabling the solderless assembly of electronics using a selection of hardware modules. There is some focus on rapid prototyping of the physical enclosure fabrication using computer-aided design.
The .NET Gadgeteer core is built upon the .NET Micro Framework, currently version 4.1 and originates from Microsoft Research in Cambridge, UK.[3] The core libraries are published under the Apache License 2.0 License and the hardware designs are under the Creative Commons 3.0 License. The core source code is publicly available from the codeplex source repository.[4]
Construction
.NET Gadgeteer projects consist of a mainboard and a series of modules connected via a standard 10 pin connector. The mainboard sockets can support one or more different types of modules, shown by a series of letters next to the socket. Each module has a letter showing its module type. (Connecting modules incorrectly does not harm the hardware – providing only one red power module is used). Any module that supplies power (via USB, DC or battery) is coloured red to help prevent multiple power sources that can potentially harm the devices.
Many different modules are currently available for a series of hardware vendors, including wireless transmission, environment sensors, actuators and custom community modules resulting in a large ecosystem of projects.
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
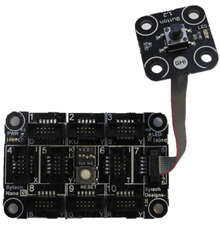
.NET Gadgeteer mainboard and button module.
Hardware
Any hardware manufacturer, builder or hobbyist can create .NET Gadgeteer-compatible hardware; currently multiple manufacturers participate.
| Mainboard | Clock speed (MHz) | Processor | Cores | Number of sockets | Width (mm) | Length (mm) | Manufacturer |
| Argon R1 | 120 | LPC1788 Cortex-M3 | 1 | 14 | 57 | 92 | Love Electronics |
| Eth Mainboard 1.0 | 168 | STM32F407 Cortex-M4 | 1 | 8 | 42 | 57 | Mountaineer Group |
| USB Mainboard 1.0 | 168 | STM32F407 Cortex-M4 | 1 | 9 | 32 | 57 | Mountaineer Group |
| Nano | 200 | Freescale ARM920T | 1 | 10 | 42 | 57 | Sytech Design |
| FEZ Spider | 73 | ARM7 LPC2478 | 1 | 14 | 52 | 57 | GHI Electronics |
| FEZ Hydra | 200 | ARM9 AT91SAMRL | 1 | 14 | 62 | 87 | GHI Electronics |
| FEZ Cerberus | 168 | STM32F405 Cortex-M4 | 1 | 8 | 47 | 57 | GHI Electronics |
| FEZ Cebuino Bee | 168 | STM32F405 Cortex-M4 | 1 | 3 | 55 | 80 | GHI Electronics |
| Bambino 200 | 204 | LPC4330 Cortex-M4 & M0 | 2 | 5 | 58 | 102 | Micromint |
| Bambino 200E | 204 | LPC4330 Cortex-M4 & M0 | 2 | 10 | 58 | 102 | Micromint |
See also
References
|
|---|
| | Main | |
|---|
| | Architectures | |
|---|
| | Families |
|
|---|
| | Interfaces |
|
|---|
| | Simulators | |
|---|
| | Lists | |
|---|
| | See also | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| | Concepts | |
|---|
| | Technologies | |
|---|
| | Platforms | |
|---|
| | Applications | |
|---|
| | Pioneers | |
|---|
| | Other | |
|---|
|
