Zolazepam
 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 4-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3,8-trimethyl-6,8-dihydropyrazolo[3,4-e][1,4]diazepin-7(1H)-one | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Legal status | ? |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 31352-82-6 |
| ATC code | None |
| PubChem | CID 35775 |
| ChemSpider | 32907 |
| UNII | G1R474U58U |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C15H15FN4O |
| Mol. mass | 286.304 |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
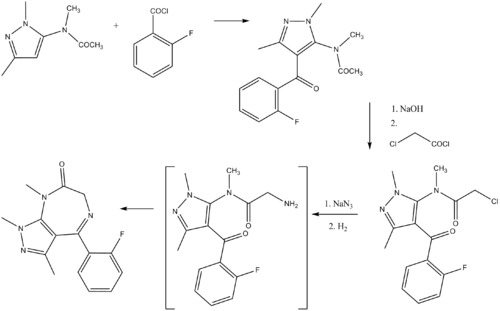
Zolazepam was discovered by a team at Parke-Davis in the 1960s.[1](Flupyrazapon) is a pyrazolodiazepinone derivative structurally related to the benzodiazepine drugs, which is used as an anaesthetic for a wide range of animals in veterinary medicine. Zolazepam is usually administered in combination with other drugs such as the NMDA antagonist tiletamine or the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist xylazine, depending on what purpose it is being used for. It is around 4 times the potency of diazepam (0.32mg/Kg vs 1.2mg/Kg in animal models) but it is both water-soluble and un-ionized at physiological pH meaning that its onset is very fast.[2]
Zolazepam was developed by Horace A. de Wald and Donald E. Butler for Parke Davis and was the result of a very detailed analysis of the benzodiazepine structure (US Patent 3,558,605 filed in 1969).
Zolazepam, in combination with tiletamine, has been used in the tranquilization of wild animals, such as gorillas and polar bears, and has been found to be superior to ketamine because of reduced side-effects.[3][4] A 1:1 mixture of Zolazepam and tiletamine is sold under the name Telazol.
See also
References
- ↑ DE Patent 2023453
- ↑ J. Med. Chem., 1977, 20 (12), pp 1562–1569 'Pyrazolodiazepines. 2. 4-Aryl-1,3-dialkyl-6,8-dihydropyrazolo[3,4-e][1,4]diazepin-7(1H)-ones as antianxiety and anticonvulsant agents'
- ↑ Sleeman JM; Cameron K, Mudakikwa AB, Nizeyi JB, Anderson S, Cooper JE, Richardson HM, Macfie EJ, Hastings B, Foster JW. (March 2000). "Field anesthesia of free-living mountain gorillas (Gorilla gorilla beringei) from the Virunga Volcano region, Central Africa.". Journal of zoo and wildlife medicine : official publication of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians. 31 (1): 9–14. PMID 10884117.
- ↑ Cattet MR; Caulkett NA, Polischuk SC, Ramsay MA. (September 1999). "Anesthesia of polar bears (Ursus maritimus) with zolazepam-tiletamine, medetomidine-ketamine, and medetomidine-zolazepam-tiletamine.". Journal of zoo and wildlife medicine : official publication of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians. 30 (3): 354–60. PMID 10572857.