Zodiac
| Astrology |
|---|
 New millennium astrological chart |
| Background |
| Traditions |
| Branches |
|
|
In both astrology and historical astronomy, the zodiac (Greek: ζῳδιακός, zōidiakos) is a circle of twelve 30° divisions of celestial longitude that are centered upon the ecliptic: the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets also remain close to the ecliptic, within the belt of the zodiac, which extends 8-9° north or south of the ecliptic, as measured in celestial latitude. Because the divisions are regular, they do not correspond exactly to the twelve constellations after which they are named.
Historically, these twelve divisions are called signs. Essentially, the zodiac is a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate system, which takes the ecliptic as the origin of latitude, and the position of the sun at vernal equinox as the origin of longitude.
Usage
The zodiac was in use by the Roman era, based on concepts inherited by Hellenistic astronomy from Babylonian astronomy of the Chaldean period (mid-1st millennium BC), which, in turn, derived from an earlier system of lists of stars along the ecliptic.[1] The construction of the zodiac is described in Ptolemy's vast 2nd century AD work, the Almagest.[2]
The term zodiac derives from Latin zōdiacus, which in its turn comes from the Greek ζῳδιακὸς κύκλος (zōdiakos kyklos), meaning "circle of animals", derived from ζῴδιον (zōdion), the diminutive of ζῷον (zōon) "animal". The name is motivated by the fact that half of the signs of the classical Greek zodiac are represented as animals (besides two mythological hybrids).
Although the zodiac remains the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system in use in astronomy besides the equatorial one,[3] the term and the names of the twelve signs are today mostly associated with horoscopic astrology.[4] The term "zodiac" may also refer to the region of the celestial sphere encompassing the paths of the planets corresponding to the band of about eight arc degrees above and below the ecliptic. The zodiac of a given planet is the band that contains the path of that particular body; e.g., the "zodiac of the Moon" is the band of five degrees above and below the ecliptic. By extension, the "zodiac of the comets" may refer to the band encompassing most short-period comets.[5]
History
Early history

The division of the ecliptic into the zodiacal signs originates in Babylonian ("Chaldean") astronomy during the first half of the 1st millennium BC, likely during Median/"Neo-Babylonian" times (7th century BC),[6] The classical zodiac is a modification of the MUL.APIN catalogue, which was compiled around 1000 BC. Some of the constellations can be traced even further back, to Bronze Age (Old Babylonian) sources, including Gemini "The Twins", from MAŠ.TAB.BA.GAL.GAL "The Great Twins", and Cancer "The Crab", from AL.LUL "The Crayfish", among others.
Babylonian astronomers at some stage during the early 1st millennium BC divided the ecliptic into twelve equal zones of celestial longitude to create the first known celestial coordinate system: a coordinate system that boasts some advantages over modern systems (such as the equatorial coordinate system). The Babylonian calendar as it stood in the 7th century BC assigned each month to a sign, beginning with the position of the Sun at vernal equinox, which, at the time, was depicted as the Aries constellation ("Age of Aries"), for which reason the first sign is still called "Aries" even after the vernal equinox has moved away from the Aries constellation due to the slow precession of the Earth's axis of rotation.[7]
Because the division was made into equal arcs, 30º each, they constituted an ideal system of reference for making predictions about a planet's longitude. However, Babylonian techniques of observational measurements were in a rudimentary stage of evolution and it was probably beyond their capacity to define in a precise way the boundary lines between the zodiacal signs in the sky.[8] Thus, the need to use stars close to the ecliptic (±9º of latitude) as a set of observational reference points to help positioning a planet within this ecliptic coordinate system.[9] Constellations were given the names of the signs and asterisms could be connected in a way that would resemble the sign's name. Therefore, in spite of its conceptual origin, the Babylonian zodiac became sidereal.[10]
In Babylonian astronomical diaries, a planet position was generally given with respect to a zodiacal sign alone, less often in specific degrees within a sign.[11] When the degrees of longitude were given, they were expressed with reference to the 30º of the zodiacal sign, i.e., not with a reference to the continuous 360º ecliptic.[12] To the construction of their mathematical ephemerides, daily positions of a planet were not as important as the dates when the planet crossed from one zodiacal sign to the next.[13]
Knowledge of the Babylonian zodiac is also reflected in the Hebrew Bible. E. W. Bullinger interpreted the creatures appearing in the books of Ezekiel and Revelation as the middle signs of the four quarters of the Zodiac,[14][15] with the Lion as Leo, the Bull is Taurus, the Man representing Aquarius and the Eagle representing Scorpio.[16] Some authors have linked the twelve tribes of Israel with the twelve signs. Martin and others have argued that the arrangement of the tribes around the Tabernacle (reported in the Book of Numbers) corresponded to the order of the Zodiac, with Judah, Reuben, Ephraim, and Dan representing the middle signs of Leo, Aquarius, Taurus, and Scorpio, respectively.[17][18] Such connections were taken up by Thomas Mann, who in his novel Joseph and His Brothers attributes characteristics of a sign of the zodiac to each tribe in his rendition of the Blessing of Jacob.
Hellenistic and Roman era

The Babylonian star catalogs entered Greek astronomy in the 4th century BC, via Eudoxus of Cnidus.[19] [20] Babylonia or Chaldea in the Hellenistic world came to be so identified with astrology that "Chaldean wisdom" became among Greeks and Romans the synonym of divination through the planets and stars. Hellenistic astrology derived in part from Babylonian and Egyptian astrology.[21] Horoscopic astrology first appeared in Ptolemaic Egypt. The Dendera zodiac, a relief dating to ca. 50 BC, is the first known depiction of the classical zodiac of twelve signs.
Particularly important in the development of Western horoscopic astrology was the astrologer and astronomer Ptolemy, whose work Tetrabiblos laid the basis of the Western astrological tradition.[22] Under the Greeks, and Ptolemy in particular, the planets, Houses, and signs of the zodiac were rationalized and their function set down in a way that has changed little to the present day.[23] Ptolemy lived in the 2nd century AD, three centuries after the discovery of the precession of the equinoxes by Hipparchus around 130 BC, but he ignored the problem by dropping the concept of a fixed celestial sphere and adopting what is referred to as a tropical coordinate system instead.
Hindu zodiac
The Hindu zodiac uses the sidereal coordinate system, which makes reference to the fixed stars. The Tropical zodiac (of Mesopotamian origin) is divided by the intersections of the ecliptic and equator, which shifts in relation to the backdrop of fixed stars at a rate of 1° every 72 years, creating the phenomenon known as precession of the equinoxes. The Hindu zodiac, being sidereal, does not maintain this seasonal alignment, but there are still similarities between the two systems. The Hindu zodiac signs and corresponding Greek signs sound very different, being in Sanskrit and Greek respectively, but their symbols are nearly identical. For example, dhanu means "bow" and corresponds to Sagittarius, the "archer", and kumbha means "water-pitcher" and corresponds to Aquarius, the "water-carrier".
Middle Ages

The High Middle Ages saw a revival of Greco-Roman magic, first in Kabbalism and later continued in Renaissance magic. This included magical uses of the zodiac, as found, e.g., in the Sefer Raziel HaMalakh.
The zodiac is found in mediaeval stained glass as at Angers Cathedral, where the master glassmaker, André Robin, made the ornate rosettes for the North and South transepts after the fire there in 1451.[24]
Early modern

An example of the use of signs as astronomical coordinates may be found in the Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris for the year 1767. The "Longitude of the Sun" columns show the sign (represented as a digit from 0 to and including 11), degrees from 0 to 29, minutes, and seconds.[25]
The zodiacal symbols are Early Modern simplifications of conventional pictorial representations of the signs, attested since Hellenistic times.
The twelve signs
What follows is a list of the twelve signs of the modern zodiac (with the ecliptic longitudes of their first points), where 0° Aries is understood as the vernal equinox, with their Latin, Greek, Sanskrit, and Babylonian names (but note that the Sanskrit and the Babylonian name equivalents denote the constellations only, not the tropical zodiac signs). Also, the "English translation" is not usually used by English speakers. The Latin names are standard English usage.
| № | Symbol | Long. | Latin name | English translation | Greek name | Sanskrit name | Sumero-Babylonian name[26] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ♈ | 0° | Aries | The Ram | Κριός (Krios) | Meṣha (मेष) | MUL LU.ḪUŊ.GA "The Agrarian Worker", Dumuzi |
| 2 | ♉ | 30° | Taurus | The Bull | Ταῦρος (Tavros) | Vṛiṣhabha (वृषभ) | MULGU4.AN.NA "The Steer of Heaven" |
| 3 | ♊ | 60° | Gemini | The Twins | Δίδυμοι (Didymoi) | Mithuna (मिथुन) | MULMAŠ.TAB.BA.GAL.GAL "The Great Twins" (Castor and Pollux) |
| 4 | ♋ | 90° | Cancer | The Crab | Καρκῖνος (Karkinos) | Karkaṭa (कर्कट) | MULAL.LUL "The Crayfish" |
| 5 | ♌ | 120° | Leo | The Lion | Λέων (Leōn) | Siṃha (सिंह) | MULUR.GU.LA "The Lion" |
| 6 | ♍ | 150° | Virgo | The Maiden | Παρθένος (Parthenos) | Kanyā (कन्या) | MULAB.SIN "The Furrow"; "The Furrow, the goddess Shala's ear of corn" |
| 7 | ♎ | 180° | Libra | The Scales | Ζυγός (Zygos) | Tulā (तुला) | MULZIB.BA.AN.NA "The Scales" |
| 8 | ♏ | 210° | Scorpio | The Scorpion | Σκoρπιός (Skorpios) | Vṛśhchika (वृश्चिक) | MULGIR.TAB "The Scorpion" |
| 9 | ♐ | 240° | Sagittarius | The (Centaur) Archer | Τοξότης (Toxotēs) | Dhanuṣha (धनुष) | MULPA.BIL.SAG, Nedu "soldier" |
| 10 | ♑ | 270° | Capricorn | "Goat-horned" (The Sea-Goat) | Αἰγόκερως (Aigokerōs) | Makara (मकर) | MULSUḪUR.MAŠ "The Goat-Fish" of Enki |
| 11 | ♒ | 300° | Aquarius | The Water-Bearer | Ὑδροχόος (Hydrokhoos) | Kumbha (कुम्भ) | MULGU.LA "The Great One", later qâ "pitcher" |
| 12 | ♓ | 330° | Pisces | The Fishes[27] | Ἰχθύες (Ikhthyes) | Mīna (मीन) | MULSIM.MAḪ "The Tail of the Swallow", later DU.NU.NU "fish-cord" |
Constellations

The zodiacal signs are distinct from the constellations associated with them, not only because of their drifting apart due to the precession of equinoxes but also because the physical constellations take up varying widths of the ecliptic, so the sun is not in each constellation for the same amount of time.[28]:25 Thus, Virgo takes up five times as much ecliptic longitude as Scorpius. The zodiacal signs are an abstraction from the physical constellations, and each represent exactly one twelfth of the full circle, or the longitude traversed by the Sun in about 30.4 days.[29]
Some "parazodiacal" constellations are also touched by the paths of the planets. The MUL.APIN lists Orion, Perseus, Auriga, and Andromeda. Furthermore, there are a number of constellations mythologically associated with the zodiacal ones : Piscis Austrinus, The Southern Fish, is attached to Aquarius. In classical maps, it swallows the stream poured out of Aquarius' pitcher, but perhaps it formerly just swam in it. Aquila, The Eagle, was possibly associated with the zodiac by virtue of its main star, Altair.[citation needed] Hydra in the Early Bronze Age marked the celestial equator and was associated with Leo, which is shown standing on the serpent on the Dendera zodiac.[citation needed] Corvus is the Crow or Raven mysteriously perched on the tail of Hydra.
Due to the constellation boundaries being redefined in 1930 by the International Astronomical Union, the path of the ecliptic now officially passes through thirteen constellations: the twelve traditional 'zodiac constellations' plus Ophiuchus, the bottom part of which interjects between Scorpio and Sagittarius. Ophiuchus is an anciently recognized constellation, catalogued along with many others in Ptolemy's Almagest, but not historically referred to as a zodiac constellation.[30][31] The inaccurate description of Ophiuchus as a sign of the zodiac drew media attention in 1995, when the BBC Nine O'Clock News reported that "an extra sign of the zodiac has been announced by the Royal Astronomical Society".[32] There had been no such announcement, and the report had merely sensationalized the 67-year-old 'news' of the IAU's decision to alter the number of designated ecliptic constellations.[33][34]
Table of dates
The following table compares the Gregorian dates on which the Sun enters
- a sign in the Ptolemaic tropical zodiac
- a sign in the Hindu sidereal system
- the astronomical constellation of the same name as the sign, with constellation boundaries as defined in 1930 by the International Astronomical Union.
The theoretical beginning of Aries is the moment of vernal equinox, and all other dates shift accordingly. The precise Gregorian times and dates vary slightly from year to year as the Gregorian calendar shifts relative to the tropical year.[35] These variations remain within less than two days' difference in the recent past and the near-future, vernal equinox in UT always falling either on 20 or 21 March in the period of 1797 to 2043, falling on 19 March in 1796 the last time and in 2044 the next.[36]
| Sign[37] | Constellation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | Tropical zodiac (2011) |
Sidereal zodiac (2011) |
Name | IAU boundaries[38] | Solar stay[38] | Brightest star |
| Aries | |
21 March – 20 April |
15 April - 15 May |
Aries | 19 April – 13 May | 25 days | Hamal |
| Taurus | |
21 April – 21 May |
16 May - 15 June |
Taurus | 14 May – 19 June | 37 days | Aldebaran |
| Gemini | |
22 May – 21 June |
16 June - 15 July |
Gemini | 20 June – 20 July | 31 days | Pollux |
| Cancer | |
22 June – 22 July |
16 July - 15 August |
Cancer | 21 July – 9 August | 20 days | Al Tarf |
| Leo | |
23 July – 22 August |
16 August - 15 September |
Leo | 10 August – 15 September | 37 days | Regulus |
| Virgo | |
23 August – 23 September |
16 September - 15 October |
Virgo | 16 September – 30 October | 45 days | Spica |
| Libra | |
24 September – 23 October |
16 October - 15 November |
Libra | 31 October – 22 November | 23 days | Zubeneschamali |
| Scorpio | |
24 October – 22 November |
16 November - 15 December |
Scorpius | 23 November – 29 November | 7 days | Antares |
| |
Ophiuchus | 30 November – 17 December | 18 days | Rasalhague | |||
| Sagittarius | |
23 November – 21 December |
16 December - 14 January |
Sagittarius | 18 December – 18 January | 32 days | Kaus Australis |
| Capricorn | |
22 December – 20 January |
15 January – 14 February |
Capricornus | 19 January – 15 February | 28 days | Deneb Algedi |
| Aquarius | |
21 January – 19 February |
15 February - 14 March |
Aquarius | 16 February – 11 March | 24 days | Sadalsuud |
| Pisces | |
20 February – 20 March |
15 March - 14 April |
Pisces | 12 March – 18 April | 38 days | Eta Piscium |
Because the Earth's axis is at an angle, some signs take longer to rise than others, and the farther away from the equator the observer is situated, the greater the difference. Thus, signs are spoken of as "long" or "short" ascension.[39]
Precession of the equinoxes
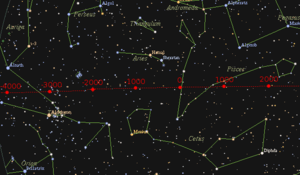
The zodiac system was developed in Babylonia, some 2,500 years ago, during the "Age of Aries".[40] At the time, it is assumed, the precession of the equinoxes was unknown, as the system made no allowance for it. Contemporary use of the coordinate system is presented with the choice of interpreting the system either as sidereal, with the signs fixed to the stellar background, or as tropical, with the signs fixed to the point of vernal equinox.[41]
Western astrology takes the tropical approach, whereas Hindu astrology takes the sidereal one. This results in the originally unified zodiacal coordinate system drifting apart gradually, with a clockwise(westward) precession of 1.4 degrees per century.
For the tropical zodiac used in Western astronomy and astrology, this means that the tropical sign of Aries currently lies somewhere within the constellation Pisces ("Age of Pisces").
The sidereal coordinate system takes into account the ayanamsa, a Sanskrit word where literally ayan means transit or movement and amsa means small part i.e. movement of equinoxes in small parts. It is unclear when Indians became aware of the precession of the equinoxes, but Bhaskar-ii in Siddhanta Shiromani gives equations for measurement of precession of equinoxes, and says his equations are based on some lost equations of Suryasiddhanta plus the equation of Munjaala.
It is not entirely clear how the Hellenistic astronomers responded to this phenomenon of precession once it had been discovered by Hipparchus around 130 BC. Today, some read Ptolemy as dropping the concept of a fixed celestial sphere and adopting what is referred to as a tropical coordinate system instead: in other words, one fixed to the Earth's seasonal cycle rather than the distant stars.
Some modern Western astrologers, such as Cyril Fagan, have advocated abandoning the tropical system in favour of a sidereal one.[42]
In modern astronomy
The zodiac is a spherical celestial coordinate system. It designates the ecliptic as its fundamental plane and the position of the Sun at Vernal equinox as its prime meridian.
In astronomy, the zodiacal constellations are a convenient way of marking the ecliptic (the Sun's path across the sky) and the path of the moon and planets along the ecliptic. Modern astronomy still uses tropical coordinates for predicting the positions the Sun, Moon, and planets, except longitude in the ecliptic coordinate system is numbered from 0° to 360°, not 0° to 30° within each sign. Longitude within individual signs was still being used as late as 1740 by Jacques Cassini in his Tables astronomiques.
Zodiac is also used to refer to the zodiacal cloud of dust grains that move among the planets and the zodiacal light that originates from their scattering of sunlight.
Unlike the zodiac signs in astrology, which are all thirty degrees in length, the astronomical constellations vary widely in size. The boundaries of all the constellations in the sky were set by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1930. This was, in essence, a mapping exercise to make the work of astronomers more efficient, and the boundaries of the constellations are not therefore in any meaningful sense an 'equivalent' to the zodiac signs. Along with the twelve original constellations, the boundaries of a thirteenth constellation, Ophiuchus (the serpent bearer), were set by astronomers within the bounds of the zodiac.
Determining Zodiac signs of planets and the Sun


In astrology, each planet and the sun have a corresponding zodiac sign that is determined by their location relative to Earth at the time of one's birth.[43]
Mnemonics
There are many mnemonics for remembering the 12 signs of the zodiac in order. A traditional mnemonic:[44]
The ram, the bull, the heavenly twins,
And next the crab, the lion shines,
The virgin and the scales,
The scorpion, archer, and the goat,
The man who holds the watering-pot,
And fish with glittering scales.
A less poetic, but succinct mnemonic is the following:[45]
The Ramble Twins Crab Liverish;
Scaly Scorpions Are Good Water Fish.
Mnemonics in which the initials of the words correspond to the initials of the star signs (Latin, English, or mixed):
All The Great Constellations Live Very Long Since Stars Can't Alter Physics.[1]
Cite error: There are <ref> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist}} template (see the help page).
As The Great Cook Likes Very Little Salt, She Compensates Adding Pepper.
Really Boring Teachers Can Live Very Sadly Since Apples Give Worthless Feelings.
All That Gold Can Load Very Lazy Students Since Children Are at Play
Unicode characters
In Unicode, the symbols are encoded in block Miscellaneous Symbols:[46]
- U+2648 ♈ aries (HTML:
♈) - U+2649 ♉ taurus (HTML:
♉) - U+264A ♊ gemini (HTML:
♊) - U+264B ♋ cancer (HTML:
♋) - U+264C ♌ leo (HTML:
♌) - U+264D ♍ virgo (HTML:
♍) - U+264E ♎ libra (HTML:
♎) - U+264F ♏ scorpius (HTML:
♏) - U+2650 ♐ sagittarius (HTML:
♐) - U+2651 ♑ capricorn (HTML:
♑) - U+2652 ♒ aquarius (HTML:
♒) - U+2653 ♓ pisces (HTML:
♓)
See also
- Alexander A. Gurshtein
- Astronomical symbols
- Circle of stars
- Cusp (astrology)
- Elements of the zodiac
References
- ↑ see MUL.APIN. See also Lankford, John. History of Astronomy, Routledge, 1996. ISBN 978-0-8153-0322-0P.43, books.google.co.uk
- ↑ Ptolemy, Claudius (1998). The Almagest. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-00260-6. Translated and annotated by G. J. Toomer; with a foreword by Owen Gingerich.
- ↑ Shapiro, Lee T. "Constellations in the zodiac." NASA. April 27, 2011.
- ↑ B. L. van der Waerden, "History of the zodiac", Archiv für Orientforschung 16 (1953) 216–230.
- ↑ OED, citing J. Harris, Lexicon Technicum (1704): "Zodiack of the Comets, Cassini hath observed a certain Tract [...] within whose Bounds [...] he hath found most Comets [...] to keep."
- ↑ Powell 2004
- ↑ Hugh Thurston, Early Astronomy, (New York: Springer-Verlag, 1994), p. 135–137.
- ↑ Sachs (1948), p. 289.
- ↑ Rochberg (1998), pp. 31.
- ↑ Rochberg (1998), pp. 17, 19.
- ↑ Rochberg (1998), p. 7.
- ↑ Rochberg (1998), p. 17.
- ↑ Rochberg (1998), p. 8.
- ↑ E.W. Bullinger, The Witness of the Stars
- ↑ D. James Kennedy, The Real Meaning of the Zodiac.
- ↑ Richard Hinckley Allen, Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning, Vol. 1 (New York: Dover Publications, 1899, p. 213-215.) argued for Scorpio having previously been called Eagle. for Scorpio.
- ↑ Ernest L. Martin, The Birth of Christ Recalculated (Pasadena, California: Foundation for Biblical Research, second ed., 1980), p. 167ff.
- ↑ D. Guthrie, J.A. Motyer (ed.), The New Bible Commentary (Grand Rapids: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Co., third ed., 1970) p. 173.
- ↑ Rogers, John H. "Origins of the ancient constellations: I. The Mesopotamian traditions." Journal of the British Astronomical Assoc. 108.1 (1998): 9–28. Astronomical Data Service.
- ↑ Rogers, John H. "Origins of the ancient constellations: II. The Mesopotamian traditions." Journal of the British Astronomical Assoc. 108.2 (1998): 79–89. Astronomical Data Service.
- ↑ Powell, Robert, Influence of Babylonian Astronomy on the Subsequent Defining of the Zodiac (2004), PhD thesis, summarized by anonymous editor, Wayback version.
- ↑ Saliba, George, 1994. A History of Arabic Astronomy: Planetary Theories During the Golden Age of Islam. New York: New York University Press. ISBN 978-0-8147-8023-7. Page 67.
- ↑ Derek and Julia Parker, Ibid, p16, 1990
- ↑ King, David. 'Angers Cathedral’, (book review of Karine Boulanger’s 2010 book, Les Vitraux de la Cathédrale d’Angers, the 11th volume of the Corpus Vitrearum series from France), Vitemus: the only on-line magazine devoted to medieval stained glass, Issue 48, February 2011, retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ↑ Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris for the year 1767. London: Board of Longitude, 1766.
- ↑ MUL.APIN; Peter Whitfield, History of Astrology (2001); W. Muss-Arnolt, The Names of the Assyro-Babylonian Months and Their Regents, Journal of Biblical Literature (1892).
- ↑ American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language 3rd ed., s.v. "Pisces."
- ↑ James, Edward W. (1982). Patrick Grim, ed. Philosophy of science and the occult. Albany: State University of New York Press. ISBN 0873955722.
- ↑ 30.4368 SI days or 2629743 seconds in tropical astrology and 30.4380 SI days or 2629846 seconds in sidereal astrology on average (the time spent by the Sun in each sign varies slightly due to the eccentricity of the Earth's orbit).
- ↑ Peters, Christian Heinrich Friedrich and Edward Ball Knobel. Ptolemy's Catalogue of Stars: a revision of the Almagest. Carnegie Institution of Washington, 1915.
- ↑ Ptolemy (2nd cent.). "VII.5". In R. Catesby Taliaferro. Almagest (1982 ed.). p. 239. Ptolemy refers to the constellation as Septentarius 'the serpent holder'.
- ↑ Kollerstrom, N. (October 1995). "Ophiuchus and the media". The Observatory (KNUDSEN; OBS) 115: 261–262. Bibcode:1995Obs...115..261K. Reproduced online at SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS), retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ↑ Kollerstrom, N. (October 1995). "Ophiuchus and the media". The Observatory (KNUDSEN; OBS) 115: 261–262. Bibcode:1995Obs...115..261K.
- ↑ The notion received further international media attention in January 2011, when it was reported that astronomer Parke Kunkle, a board-member of the Minnesota Planetarium Society, had suggested that Ophiuchus was the zodiac's '13th sign'. He later issued a statement to say he had not reported that the zodiac ought to include 13 signs instead of 12, but was only mentioning that there were 13 constellations; reported in Mad Astronomy: Why did your zodiac sign change? 13 January 2011.
- ↑ The Gregorian calendar is built to satisfy the First Council of Nicaea, which placed vernal equinox is on 21 March, but it is not possible to keep it on a single day within a reasonable system of leap days.
- ↑ See Jean Meeus, Astronomical Tables of the Sun, Moon, and Planets, 1983 published by Willmann-Bell, Inc., Richmond, Virginia. The date in other time zones may vary.
- ↑ Jackson Swift. "Astrology: Tropical Zodiac and Sidereal Zodiac". goarticles.com. Retrieved 2013-11-10.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 The Real Constellations of the Zodiac. Dr. Lee T. Shapiro, director of Morehead Planetarium University of North Carolina (Spring 1977)
- ↑ Julia Parker "The Astrologer's Handbook", pp 10, Alva Press, NJ, 2010
- ↑ Sachs, Abraham (1948), "A Classification of the Babylonian Astronomical Tablets of the Seleucid Period", Journal of Cuneiform Studies, Vol. 2, No. 4, pp. 271–290
- ↑ Rochberg, Francesca (1998), "Babylonian Horoscopes", American Philosophical Society, New Series, Vol. 88, No. 1, pp i-164
- ↑ Cyril Fagan Gale Encyclopedia of Occultism & Parapsychology, 2012
- ↑ Horoscope Dates "Determining the Zodiac signs of planets", 2004. Retrieved on 18 April 2013.
- ↑ Project Gutenberg ebook "An Alphabet Of Old Friends"; see Z for Zodiac.
- ↑ Rey, H.A. (1952). The Stars, Houghton Mifflin.
- ↑ "Zodiacal symbols in Unicode block Miscellaneous Symbols". The Unicode Standard>date=2010.
External links
![]() Media related to Zodiac at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Zodiac at Wikimedia Commons
- "A Treatise on Zodiacal Signs and Constallations: Unique Jewels on the Benefits of Keeping Time" is a manuscript that dates back to 1831 with a focus on Arabic, Coptic and Syriac calendars.
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||