Zeranol
| Zeranol | |
|---|---|
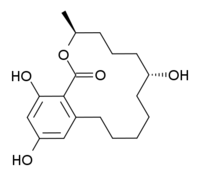 | |
| IUPAC name (3S,7R)-7,14,16-Trihydroxy-3-methyl-3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-decahydro-1H-2-benzoxacyclotetradecin-1-one | |
| Other names α-Zearalanol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 26538-44-3 |
| PubChem | 33534 |
| ChemSpider | 4447689 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL371463 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C[C@H]1CCCC(CCCCCC2=CC(=CC(=C2C(=O)O1)O)O)O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C18H26O5 |
| Molar mass | 322.40 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Zeranol (α-zearalanol) is a non-steroidal estrogen agonist. It is a mycotoxin, derived from fungi in the Fusarium family, and may be found as a contaminant in fungus-infected crops. It is 3-4x more potent as an estrogen agonist than the related compound zearalenone.[1]
Zeranol is approved for use as a growth promoter in livestock, including beef cattle, in the United States. In Canada, it is approved for use in beef cattle only.[2] Its application is not approved for use in the European Union.
Zeranol increases cancer cell proliferation in already existing breast cancer.[3] There are mixed results to whether zeranol has anticancer or carcinogenic properties in non cancer containing breast cells depending on dose.[3] Overall evidence points to zeranol being a risk factor and promoter for cancer.[3] However, dietary exposure from the use of zeranol-containing implants in cattle is insignificant.[4]
References
- ↑ Mirocha, CJ; Schauerhamer, B; Christensen, CM; Niku-Paavola, ML; Nummi, M (1979). "Incidence of zearalenol (Fusarium mycotoxin) in animal feed". Applied and environmental microbiology 38 (4): 749–50. PMC 243572. PMID 161492.
- ↑ Health Canada, Questions and Answers - Hormonal Growth Promoters
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Ye, Weiping et al. (February 2011). "Zeranol Down-Regulates p53 Expression in Primary Cultured Human Breast Cancer Epithelial Cells through Epigenetic Modification". Int J Mol Sci 12 (3): 1519–1532. doi:10.3390/ijms12031519.
- ↑ Lindsay DG (August 1985). "Zeranol--a 'nature-identical' oestrogen?". Food Chem Toxicol 23 (8). pp. 767–74.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||