Yuncheng
| Yuncheng 运城 | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
运城市 | |
 | |
 | |
 Yuncheng | |
| Coordinates: 35°01′00″N 110°59′00″E / 35.01667°N 110.98333°ECoordinates: 35°01′00″N 110°59′00″E / 35.01667°N 110.98333°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Shanxi |
| County-level divisions | 13 |
| Municipal seat | Yanhu District |
| Government | |
| • Type | Prefecture-level city |
| • CPC Yuncheng Secretary | Bai Yun (白云) |
| • Mayor | Wang Anpang (王安庞) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 14,106 km2 (5,446 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,237 km2 (478 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 370 m (1,210 ft) |
| Population (2010)[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 5,134,794 |
| • Density | 360/km2 (940/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 680,043 |
| • Urban density | 550/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | China Standard (UTC+8) |
| Postal code | 044000 |
| Area code(s) | 0359 |
| License Plate | 晋M |
| Administrative division code | 140800 |
| ISO 3166-2 | CN-14-08 |
Yùnchéng (simplified Chinese: 运城; traditional Chinese: 運城) is the southernmost prefecture-level city in Shanxi province, People's Republic of China. It borders Linfen and Jincheng municipalities to the north and east, and Henan and Shaanxi provinces to the south and west.
The Olympic Torch Relay went through this city 25 June 2008 on its way to Beijing.
History
In early China, it was the location of the state of Kunwu (昆吾).
Administration
The Municipal executive, legislature and judiciary are in Yanhu District (盐湖区), together with the CPC and Public Security Bureau.
| Map | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
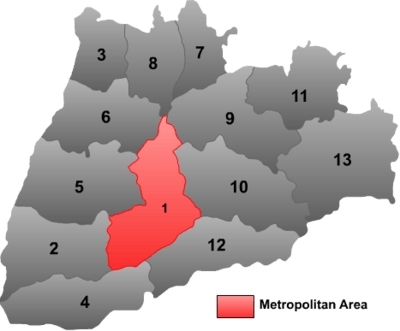 | ||||||
| # | Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2003 est.) | Area (km²) | Density (/km²) |
| 1 | Yanhu District | 盐湖区 | Yánhú Qū | 620,000 | 1,237 | 501 |
| 2 | Yongji City | 永济市 | Yǒngjì Shì | 430,000 | 1,221 | 352 |
| 3 | Hejin City | 河津市 | Héjīn Shì | 360,000 | 593 | 607 |
| 4 | Ruicheng County | 芮城县 | Ruìchéng Xiàn | 380,000 | 1,161 | 327 |
| 5 | Linyi County | 临猗县 | Línyī Xiàn | 530,000 | 1,350 | 393 |
| 6 | Wanrong County | 万荣县 | Wànróng Xiàn | 420,000 | 1,037 | 405 |
| 7 | Xinjiang County | 新绛县 | Xīnjiàng Xiàn | 320,000 | 600 | 533 |
| 8 | Jishan County | 稷山县 | Jìshān Xiàn | 330,000 | 680 | 485 |
| 9 | Wenxi County | 闻喜县 | Wénxǐ Xiàn | 380,000 | 1,160 | 328 |
| 10 | Xia County | 夏县 | Xià Xiàn | 350,000 | 1,328 | 264 |
| 11 | Jiang County | 绛县 | Jiàng Xiàn | 270,000 | 968 | 279 |
| 12 | Pinglu County | 平陆县 | Pínglù Xiàn | 250,000 | 1,151 | 217 |
| 13 | Yuanqu County | 垣曲县 | Yuánqǔ Xiàn | 220,000 | 1,620 | 136 |
Geography
Yuncheng has a continental, monsoon-influenced semi-arid climate (Köppen BSk), with four distinct seasons.[2] Winters are cold and very dry, while summers are hot and humid. Monthly mean temperatures range from −0.9 °C (30.4 °F) in January to 27.4 °C (81.3 °F) in July, and the annual mean is 14.05 °C (57.3 °F). Over 60% of the annual rainfall occurs from June to September.
| Climate data for Yuncheng (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.7 (40.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
14.3 (57.7) |
21.8 (71.2) |
27.4 (81.3) |
31.8 (89.2) |
32.6 (90.7) |
31.4 (88.5) |
26.3 (79.3) |
20.2 (68.4) |
12.4 (54.3) |
6.3 (43.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.6 (21.9) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
3.0 (37.4) |
9.3 (48.7) |
14.4 (57.9) |
19.8 (67.6) |
22.7 (72.9) |
21.9 (71.4) |
16.4 (61.5) |
9.7 (49.5) |
2.1 (35.8) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
8.9 (48.1) |
| Precipitation mm (inches) | 5.0 (0.197) |
6.6 (0.26) |
20.1 (0.791) |
38.1 (1.5) |
46.6 (1.835) |
65.1 (2.563) |
110.0 (4.331) |
82.2 (3.236) |
79.2 (3.118) |
51.7 (2.035) |
20.2 (0.795) |
4.6 (0.181) |
529.4 (20.842) |
| Avg. precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2.8 | 3.0 | 4.8 | 6.4 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 9.7 | 8.7 | 9.0 | 7.6 | 4.7 | 2.4 | 74.7 |
| % humidity | 57 | 54 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 56 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 67 | 66 | 61 | 61.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 149.0 | 147.1 | 166.0 | 199.6 | 232.9 | 226.6 | 227.7 | 223.8 | 177.0 | 166.7 | 151.5 | 150.7 | 2,218.6 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 48 | 48 | 45 | 51 | 54 | 52 | 52 | 54 | 48 | 48 | 49 | 50 | 49.9 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
Transportation
Public security issues
Rural communities in Yuncheng City have been the hunting grounds of Snakeheads, Chinese human trafficking mafia. Rural children, typically middle school students fit for labour, were "recruited" with the promise of jobs in China's southwest -- Longchuan County in Yunnan's Dehong Prefecture. Once in Longchuan the children were whisked ("through sugar-cane fields on a motorcycle") over the Sino-Burmese border into Kachin State and imprisoned. They were made to sign demands for ransom (e.g. 40 - 80,000 RMB). They are subjected to torture prior to making telephone appeals home.
For the "recruiter"/kidnappers the ethno-linguistic ties between the Jingpo citizens of Dehong and those of Kachin are an enabling factor, as is the ineffectiveness of Chinese-allied Myanmar police in this region of de facto independence (Cf. Nayoubeng Mountain militia); Interpol is of even less use, as Myanmar itself is a rogue state.
According to the Chinese-language Beijing News (20 January 2009), around 50 students left Yuncheng for the Snakehead "jobs" in September–October 2008. Some boys disappeared immediately, the rest were to follow. Two families whose sons had left Yuncheng in the middle of October paid ransoms on Nov 5; these boys reappeared in Longchuan on Nov 8. Back home in Shanxi, the boys told police and reporters that one of their cellmates had been one of the earliest-disappeared Yuncheng boys, and was in a very bad way ("nothing but skin and bones .. babbling like an idiot"). Yuncheng police paid a third ransom at year's end, and one boy, disappeared in late October, was retrieved on Jan 2.[3]
Notes and references
- ↑ "2010年运城市第六次全国人口普查主要数据公报(Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China)". National Bureau of Statistics of China. Retrieved 2012-08-30.
- ↑ Updated Asian Map of the Köppen system.
- ↑ Zhang Pinghui, South China Morning Post, Teens Tell of Kidnap, Torture in Myanmar, Jan 21, 2009
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
