Xenon oxytetrafluoride
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Xenon oxytetrafluoride | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 13774-85-1 |
| ChemSpider | 10326200 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:F[Xe](F)(F)(F)=O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | XeOF4 |
| Molar mass | 223.23 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 3.17 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −46.2 °C |
| Solubility in water | Reacts with water |
| Structure | |
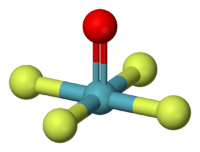
| Molecular shape | square pyramidal |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification | not listed |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Xenon oxytetrafluoride (XeOF4) is an inorganic chemical compound. As are all xenon compounds, it is extremely reactive and unstable, and hydrolyses in water to give dangerously hazardous and corrosive products, including hydrogen fluoride:
- XeOF
4 + 2 H
2O → Xe + 4 HF + 3/2 O
2
In addition, some ozone and fluorine are also formed. The reaction is extremely dangerous, and xenon oxytetrafluoride should therefore be kept away from any trace of water or water vapour under all conditions.
Reactions
XeOF4 reacts with H2O in the following steps:
- XeOF
4 + H
2O → XeO
2F
2 + 2 HF
- XeO
2F
2 + H
2O → XeO
3 + 2 HF
XeO3 is a dangerous explosive, decomposing explosively to Xe and 3/2 O2.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.