Xanthate
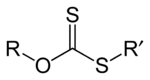
Xanthate usually refers to a salt with the formula ROCS2-M+ (R = alkyl; M+ = Na+, K+).[1] The name xanthates is derived from Greek ξανθός [ksantʰós], meaning “yellowish, golden”, and indeed most xanthate salts are yellow. These organosulfur compounds are important in two areas, the production of cellophane and related polymers from cellulose and secondly in mining for the extraction of certain ores.[2] They are also versatile intermediates in organic synthesis. Xanthates also refer to esters of xanthic acid. These esters have the structure ROC(=S)SR'.
Formation and structure
Xanthate salts are produced by the reaction of an alcohol with sodium or potassium hydroxide and carbon disulfide:[2][3]
- ROH + CS2 + KOH → ROCS2K + H2O
The reaction involves the attack of the alkoxide salt. For example, sodium ethoxide gives sodium ethyl xanthate. Virtually any alcohol can be used in this reaction. Technical grade xanthate salts are usually of 90–95% purity. Impurities include alkali-metal sulfide, sulfate, trithiocarbonates, thiosulfate, sulfite, or carbonate as well as residual raw material such as alcohol and alkali hydroxide. These salts are available commercially as powder, granules, flakes, sticks, and solutions are available. China is a major exporter of granules.
Some commercially important xanthate salts include:
- sodium ethyl xanthate (SEX), CH3CH2OCS2Na,
- potassium ethyl xanthate, CH3CH2OCS2K,
- sodium isopropyl xanthate (SIPX)
- sodium isobutyl xanthate (SIBX)
- potassium amyl xanthate (PAX)
The OCS2 core of xanthate salts and esters is characteristically planar. The central carbon is sp2-hybridized.
Reactions
Xanthate salts characteristically decompose in acid:
- ROCS2K + HCl → ROH + CS2 + KCl
This reaction is the reverse of the method for the preparation of the xanthate salts. The intermediate in the decomposition is the xanthic acid, ROC(S)SH, which can be isolated in certain cases.
Xanthate anions also undergo alkylation to give xanthate esters, which are generally stable:[4]
- ROCS2K + R'X → ROC(S)SR' + KX
The C-O bond in these compounds are susceptible to cleavage by the Barton–McCombie deoxygenation, which provides a means for deoxygenation of alcohols.
Analogous to their S-alkylation, xanthates bind to transition metal cations as bidentate ligands. The neutral complexes are soluble in organic solvents.[5]
They can be oxidized to the so-called dixanthogens:
- 2 ROCS2Na + Cl2 → ROC(S)S2C(S)OR + 2 NaCl
Industrial applications
Cellulose reacts with carbon disulfide (CS2) in presence of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produces sodium cellulose xanthate, which upon neutralization with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) gives viscose rayon or cellophane paper (Sellotape or Scotch Tape).
Xanthate salts are used as flotation agents in mineral processing. They are intermediates in the Chugaev elimination process and are used to control radical polymerisation under the RAFT process, also termed MADIX (macromolecular design via interchange of xanthates).
Related compounds
Rarely encountered, thioxanthates arise by the reaction of CS2 with thiolate salts. For example, sodium ethylthioxanthate has the formula C2H5SCS2Na. Dithiocarbamates are also related compounds, and are more useful. They arise from the reaction of the amine with CS2. For example, sodium diethyldithiocarbamate has the formula (C2H5)2NCS2Na.
Environmental impacts
Xanthates may be toxic to aquatic biota at concentrations of less than 1 mg/L.[6] Water downstream of mining operations can be contaminated.[7]
References
- ↑ IUPAC does not recommend the use of the term xanthate, although it is in current use in the scientific literature: "IUPAC definition".
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kathrin-Maria Roy "Xanthates" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a28 423
- ↑ This report gives a detailed procedure for the potassium ethyl xanthate: Charles C. Price and Gardner W. Stacy (1948), "p-nitrophenyl sulfide", Org. Synth. 28: 82; Coll. Vol. 3: 667
- ↑ Fabien Gagosz and Samir Z. Zard (1948), "A Xanthate-Transfer Approach to α-Trifluoromethylamines", Org. Synth. 84: 32; Coll. Vol. 11: 212
- ↑ F. Galsbøl, C. E. Schäffer, "Tris (O-Ethyl Dithiocarbonato) Complexes of Tripositive Chromium, Indium, and Cobalt" Inorganic Syntheses 1967, Volume 10, pages 42–49.doi:10.1002/9780470132418.ch6
- ↑ Besser, J.; Brumbaugh, W.; Allert, A.; Poulton, B.; Schmitt, C.; Ingersoll, C. (2009). "Ecological impacts of lead mining on Ozark streams: toxicity of sediment and pore water". Ecotoxicology and environmental safety 72 (2): 516–526. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.05.013. PMID 18603298.
- ↑ Xu, Y.; Lay, J. P.; Korte, F. (1988). "Fate and effects of xanthates in laboratory freshwater systems". Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 41 (5): 683–689. doi:10.1007/BF02021019. PMID 3233367.