XPhos
| XPhos | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IUPAC name 2-Dicyclohexylphosphino-2′,4′,6′-triisopropylbiphenyl | |
| Other names XPhos | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 564483-18-7 |
| PubChem | 11155794 |
| ChemSpider | 9330902 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C33H49P |
| Molar mass | 476.72 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Melting point | 187-190 °C |
| Solubility in water | organic solvents |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
XPhos is an organophosphorus compound derived from biphenyl. Its palladium complexes exhibit high activity for Buchwald-Hartwig amination reactions involving aryl chlorides and aryl tosylates. Both palladium and copper complexes of the compound exhibit high activity for the coupling of aryl halides and aryl tosylates with various amides.[1] The ligand has convenient handling characteristics since it is air-stable.[2]
Structure
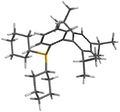
-
One view of the molecule's structure.
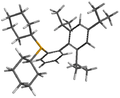
-
Another view of the molecule's structure.
See also
References
- ↑ Huang, X.; Anderson, K. W.; Zim, D.; Jiang, L.; Klapars, A.; Buchwald, S. L. (2003). "Expanding Pd-Catalyzed C-N Bond-Forming Processes: The First Amidation of Aryl Sulfonates, Aqueous Amination, and Complementarity with Cu-Catalyzed Reactions". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125 (22): 6653–6655. doi:10.1021/ja035483w. PMID 12769573.
- ↑ Altman, R.A.; Fors, B.P.; Buchwald, S.L. (2007). "Pd-Catalyzed Amination Reactions of Aryl Halides Using Bulky Biarylmonophosphine Ligands". Nature Protocols 2 (11): 2881–2887. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.414. PMID 18007623.