XO-2b
| Extrasolar planet | List of extrasolar planets | |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Parent star | ||
| Star | XO-2 (XO-2B) | |
| Constellation | Lynx[1] | |
| Right ascension | (α) | 07h 48m 06.468s [2] |
| Declination | (δ) | +50° 13′ 32.96″ [2] |
| Distance | 483 ± 33 [3] ly (148 ± 10 [3] pc) | |
| Spectral type | K0V [4] | |
| Orbital elements | ||
| Semimajor axis | (a) | 0.0369 ± 0.002 AU |
| Eccentricity | (e) | 0 |
| Orbital period | (P) | 2.61586178 ± 0.00000075[5] d |
| Inclination | (i) | 87.62 ± 0.51[5]° |
| Argument of periastron |
(ω) | ?° |
| Time of periastron | (T0) | 2454147.74902 ± 0.00002 JD |
| Semi-amplitude | (K) | 80.2 m/s |
| Physical characteristics | ||
| Mass | (m) | 0.57 ± 0.06 MJ |
| Radius | (r) | 0.973 ± 0.03 RJ |
| Density | (ρ) | 820 kg m-3 |
| Surface gravity | (g) | 1.42 m/s² |
| Temperature | (T) | 1208 K |
| Discovery information | ||
| Discovery date | 2007 | |
| Discoverer(s) | Burke et al. | |
| Discovery method | Transit (including secondary eclipse) | |
| Other detection methods | Radial velocity | |
| Discovery status | Published | |
| Database references | ||
| Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia | data | |
| SIMBAD | data | |
XO-2b (or rarely XO-2Bb) is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star XO-2 (in fact XO-2B to be precise, since XO-2 is wide binary star) in the constellation Lynx.[6] This planet was found by transit method in 2007 by Burke et al. This was the second such planet found by the XO telescope.
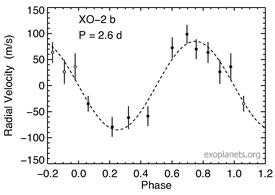
Like most planets found by the transit method, it is a roughly Jupiter sized planet that orbits very close to its host star; in this case, it has a surface temperature of about 1200 K, so it belongs to a group of exoplanets known as hot Jupiters. The planet takes 2.6 days to orbit the star at the average distance of 0.0369 AU. The planet has mass of 57% of Jupiter and radius of 97% of Jupiter. The radius is relatively large for its mass, probably due to its intense heating from its nearby star that bloats the planet’s atmosphere. The large radius for its mass gives a low density of 820 kg/m3.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Roman (1987). "Constellation boundaries". Identification of a Constellation From Position. Retrieved 2012-03-03.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hog et al. (2000). "Tyc 3413-5-1". The Tycho-2 Catalogue. Retrieved 2012-01-07.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Torres, Guillermo et al. (2008). "Improved Parameters for Extrasolar Transiting Planets". The Astrophysical Journal 677 (2): 1324–1342. arXiv:0801.1841. Bibcode:2008ApJ...677.1324T. doi:10.1086/529429.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Burke, Christopher J. et al. (2007). "XO-2b: Transiting Hot Jupiter in a Metal-rich Common Proper Motion Binary". The Astrophysical Journal 671 (2): 2115–2128. arXiv:0705.0003. Bibcode:2007ApJ...671.2115B. doi:10.1086/523087.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Sing, D. K. et al. (2011). "Gran Telescopio Canarias OSIRIS transiting exoplanet atmospheric survey: detection of potassium in XO-2b from narrowband spectrophotometry". Astronomy and Astrophysics 527. article number A73. arXiv:1008.4795. Bibcode:2011A&A...527A..73S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015579.
- ↑ XO-2 b "SIMBAD query result:XO-2b -- Extra-solar Planet Candidate". Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
External links
![]() Media related to XO-2b at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to XO-2b at Wikimedia Commons
Coordinates: ![]() 07h 48m 07s, +50° 13′ 33″
07h 48m 07s, +50° 13′ 33″