Wilhelm Keitel
| Wilhelm Keitel | |
|---|---|
 Wilhelm Keitel | |
| Birth name | Wilhelm Bodewin Gustav Keitel |
| Nickname | "Lakeitel" |
| Born |
22 September 1882 Helmscherode, Brunswick, German Empire |
| Died |
16 October 1946 (aged 64) Nuremberg, Allied-occupied Germany |
| Allegiance |
|
| Service/branch | Wehrmacht |
| Years of service | 1901–1945 |
| Rank | Generalfeldmarschall |
| Commands held | OKW |
| Battles/wars |
World War I World War II |
| Awards |
Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross Wound Badge of 20 July 1944 (in black) Golden Party Badge |
| Relations | Bodewin Keitel (brother) |
Wilhelm Bodewin Johann Gustav Keitel (22 September 1882 – 16 October 1946) was a German field marshal (Generalfeldmarschall). As head of the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (Supreme Command of the Armed Forces) and de facto war minister under Adolf Hitler, he was one of Germany's most senior military leaders during World War II. At the Allied court at Nuremberg he was tried, sentenced to death and hanged as a war criminal. He was the highest-ranking German soldier to be tried at Nuremberg.
Early life and career
Keitel was born in the village of Helmscherode near Gandersheim in the Duchy of Brunswick, the eldest son of Carl Keitel (1854–1934), a middle class landowner, and his wife Apollonia Vissering (1855–1888). After completing his education at the gymnasium in Göttingen, his plans to take over his family's estates foundered on his father's resistance. Instead he embarked on a military career in 1901, becoming a Fahnenjunker (Cadet Officer) of the Prussian Army. As a commoner he did not join the cavalry, but the mounted 46th Lower-Saxon Field Artillery Regiment in Wolfenbüttel, serving as adjutant from 1908.
In 1909, Keitel married Lisa Fontaine, a wealthy landowner's daughter from Hanover. Together they had six children, one of whom died in infancy. His eldest son, Karl-Heinz Keitel went on to serve as a divisional commander in the Waffen-SS. During World War I Keitel served on the Western Front with Field Artillery Regiment No. 46. In September 1914, during the fighting in Flanders, he was severely wounded in his right forearm by a shell fragment. Elevated to the rank of a Hauptmann (Captain), Keitel recovered, and thereafter was posted to the staff of the 19th Reserve Division in early 1915. He fought in the First Battle of the Marne, at the Eastern Front, in the Battle of Verdun, and the Battle of Passchendaele, being awarded the Iron Cross 2nd and 1st Class.
After the war, he stayed in the newly created Reichswehr of the Weimar Republic, and played a part in organising paramilitary Freikorps frontier guard units on the Polish border. Keitel also served as a divisional general staff officer of the 6th (Prussian) Artillery Regiment, and later taught at the Hanover Cavalry School for two years, from 1923 in the rank of a major. In late 1924, Keitel was transferred to the German Ministry of the Reichswehr (Reichswehrministerium) in Berlin, serving with the Troop Office (Truppenamt), the post-Versailles disguised General Staff. Three years later, he returned to the 6th Artillery Regiment as commander of the 2nd department.
As lieutenant colonel he was again assigned to the Reichswehr Ministry in 1929 and soon promoted to the head of the organisational department ("T 2"), a post he retained after the Nazi seizure of power in 1933. Playing a vital role in the German re-armament, in 1931 he at least once travelled to the Soviet Union to inspect secret Reichswehr training camps. He suffered a heart attack and double pneumonia in the autumn of 1932, followed by a longer stay at a Czechoslovak sanatorium. In 1935, based on a recommendation by Werner von Fritsch, Keitel was promoted to major general and appointed as the departmental head of the Wehrmachtsamt (Armed Forces Office) which had the responsibility over all three branches of the armed forces.
Children involved in World War II
His youngest son, Hans-Georg Keitel, was severely wounded in the thigh during the 1940 campaign in France. He died on 18 July 1941 in a field hospital after being mortally wounded the day before by a Soviet aircraft attack. Hans was buried in the family plot in Bad Gandersheim. His father's ashes (supposedly scattered after being hanged) were purchased from the Americans and are buried with him and his uncle Bodewin Keitel at the family plot in Bad Gandersheim. Another son, Major Ernst-Wilhelm Keitel, was captured by the Soviets at the end of World War II. He survived his captivity, was released in January 1956 and returned home to Germany.[1]
Role of Keitel's brother in the plot to kill Hitler
Keitel's brother, General Bodewin Keitel, an infantry general in the Army High Command (OKH), was captured by Allied forces in 1945 and released in 1947. On the day of the 20 July 1944 plot to kill Adolf Hitler, Bodewin Keitel was on an inspection tour in his command area in Danzig, when his command post inadvertently received a telex from a citizen of Berlin addressed to his first officer, Hasso von Boehmer from the conspirator's headquarters in the Bendlerblock, arranging the first steps to then be taken by participant Boehmer. When Keitel then heard a radio broadcast about the failed assassination attempt, Keitel, aware his brother Wilhelm had to have been present at the meeting with Hitler in the Wolf's Lair and could conceivably be hurt or dead, had Boehmer immediately found and arrested. Boehmer was executed on 5 March 1945 in Plötzensee prison.[2] Wilhelm Keitel was somehow not injured or killed in the bomb blast, and also was the only one present at Wolf's Lair assassination not to suffer a perforated eardrum from the bomb blast. Bodewin died in 1988 and was buried in the family plot in Bad Gandersheim in southern Lower Saxony.
OKW and World War II


In 1937, Keitel received a promotion to general. In the following year, after the Blomberg-Fritsch Affair, the Ministry of War (Reichskriegsministerium) was replaced by the Supreme Command of the Armed Forces (Oberkommando der Wehrmacht or OKW), and Keitel was appointed as its chief. This effectively made Keitel Germany's war minister, and accordingly he was appointed to the Cabinet. Soon after his appointment at OKW, he convinced Hitler to appoint his close friend, Walter von Brauchitsch, Commander-in-Chief of the Army.
For a brief period in October 1938, Keitel was Military Governor of the Sudetenland. In February 1939 Keitel again became Chief of OKW, a post he held until the end of the war. In the early years of World War Two, Keitel greatly admired Hitler. Reinhard Spitzy later said:
"Keitel was an obedient lackey of his master. He was even called "Lackeitel", We only ever called him that"[3]
During World War II, Keitel was one of the primary planners of the Wehrmacht campaigns and operations on the Western and the Eastern fronts. He advised Hitler against invading France and opposed Operation Barbarossa. Both times he backed down in the face of Hitler and tendered his resignation, which Hitler refused to accept.
In 1940, after the French campaign, he was promoted to field marshal during the 1940 Field Marshal Ceremony along with several other generals. Count Johann Kielmansegg said regarding his promotion:
"Field marshal was a bit too good for him. General was already quite nice"[4]
Unusual for a non-field commander, Keitel was awarded the Knight's Cross for arranging the armistice with France. Keitel realized the Germans would be unable to win the Battle of Britain, as the British had the backing of the almost unlimited resources of the United States.
He had advised Hitler not to attack the Soviet Union in 1941 as he was convinced that "Operation Barbarossa" would be a failure. The overwhelming success of Barbarossa in its initial phase did a great deal to undermine Keitel's authority in the face of Hitler. However, he was the author of the infamous Barbarossa decree, which condemned captured prisoners and ensured a high level of brutality by German soldiers against Russian civilians.
In 1942, he confronted Hitler in defense of Field Marshal Wilhelm List, whose Army Group A was stalled in the Battle of the Caucasus. Hitler spurned Keitel's pleading and fired List. Keitel's defense of List was his last act of defiance to Hitler; he never again challenged Hitler's orders. For example, during a strategy briefing late in the war, Luftwaffe intelligence discovered vast numbers of Soviet fighter aircraft ready to be deployed to the front. Reichsmarschall Hermann Göring, Commander-in-Chief of the Luftwaffe, told Hitler that they were simply dummies; the Red Air Force could not possibly have that many aircraft. Count Johann Kielmansegg later described it:
"There was a disagreement around around Hitler's map table and Keitel got wind of it, he was in the same room at the back, but somehow he got wind of it and I heard him say, without knowing what the issue was, "You're quite right, My Führer" I can hear him now"[5]
Keitel unquestionably allowed Heinrich Himmler a free hand with his racial controls and ensuing terror in occupied Eastern European territories. He also signed numerous orders of dubious legality under the laws of war. The most infamous were the Commissar Order (which stipulated that Soviet political commissars were to be shot on sight) and the Night and Fog Decree (which called for the forced disappearance of resistance fighters and other political prisoners in Germany's occupied territories). Another was the order that French pilots of the Normandie-Niemen squadron be executed rather than be made prisoners of war.
According to Albert Speer memoirs, nearly all of the field marshals and generals viewed him with scorn and disdain for succumbing to Hitler's influence and transforming himself from a "honorable, solidly respectable general" into a powerless yes-man with all the wrong instincts, whose only job was to allow Hitler to take control of the Army. General Ludwig Beck complained that he was incapable of giving Hitler the reality of the situations and was an extremely poor tactician whose decisions were motivated more by ensuring his own survival rather than the troops; Marshal Paul Ludwig Ewald von Kleist labeled him as nothing more than a "stupid follower of Hitler" and most commanders went out of his way to ignore his orders. Although Von Kleist did admit that had Hitler chose a more competent commander (such as himself), he would have only two weeks. His sycophancy was well known in the army, and he acquired the nickname 'Lakeitel', a pun on his name (in German, the word 'Lakai' means 'lackey').[6] Keitel accepted Hitler's directive for Operation Citadel in 1943, despite strong opposition from several field officers who argued that neither the troops nor the new tanks on which Hitler staked his hopes for victory were ready.
Keitel played an important role in foiling the 20 July plot in 1944. Keitel then sat on the Army "Court of honour" that handed over many officers who were involved, including field marshal Erwin von Witzleben, to Roland Freisler's notorious People's Court.
In April and May 1945, during the Battle of Berlin, Keitel called for counterattacks to drive back the Soviet forces and relieve Berlin. However, there were insufficient German forces to carry out such attacks.
After Hitler's suicide on 30 April, Keitel stayed on as a member of the short-lived Flensburg government under Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz. Upon arriving in Flensburg, Albert Speer found Keitel to be grovelling to Dönitz in the same way he had grovelled to Hitler.
On 8 May 1945, Dönitz authorised Keitel to sign an unconditional surrender in Berlin. Although Germany had surrendered to the Allies a day earlier, Stalin had insisted on a second surrender ceremony in Berlin.
Nazi connections

As a military officer, Keitel was prohibited by law from joining the NSDAP (Nazi Party). However, after the Wehrmacht's rapid early successes on the Russian Front, he was given a "Golden" (Honorary) NSDAP membership badge by Adolf Hitler, who was seeking to link military successes to political successes. In 1944, German laws were changed and military officers were encouraged to seek NSDAP membership. Keitel claimed he did so as a formality at the Nuremberg Trials, but never received formal party membership. He was one of only two people to receive honorary party membership status.
Before his execution, Keitel published Mein Leben: Pflichterfüllung bis zum Untergang: Hitlers Feldmarschall und Chef des Oberkommandos der Wehrmacht in Selbstzeugnissen, otherwise known in English as In the Service of the Reich, and was later re-edited as The Memoirs of Field-Marshal Keitel by Walter Görlitz from a translation by David Irving as the author in 1965. Another work by Keitel later published in English was Questionnaire on the Ardennes offensive[7]
Trial and execution


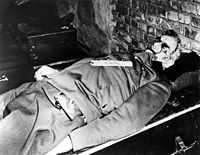
Four days after the surrender, Keitel was arrested along with the rest of the Flensburg government. He soon faced the International Military Tribunal (IMT), which indicted him on all four counts before it: conspiracy to commit crimes against peace, planning, initiating and waging wars of aggression, war crimes and crimes against humanity. Most of the case against him was based on his signature being present on dozens of orders that called for soldiers and political prisoners to be killed or disappeared.[8]
Keitel admitted that he knew many of Hitler's orders were illegal. For instance, he described the Night and Fog Decree, which ordered the disappearance of resistance fighters in the occupied territories, as "the worst of all" the orders he had been given.[9] His defence relied almost entirely on the argument that he was merely following orders in conformity to "the leader principle" (Führerprinzip) and his personal oath of loyalty to Hitler.
The IMT rejected this defence and convicted him on all charges. Although the tribunal's charter allowed "superior orders" to be considered a mitigating factor, it found that Keitel's crimes were so egregious that there were no mitigating factors. The tribunal wrote, "Superior orders, even to a soldier, cannot be considered in mitigation where crimes as shocking and extensive have been committed consciously, ruthlessly and without military excuse or justification." It also pointed out that while he claimed the Commando Order, which ordered Allied commandos to be shot without trial, was illegal, he had reaffirmed it and extended its application. It also noted several instances where he issued illegal orders on his own authority.[8]
Before the court he openly admitted his guilt in an "awful war," saying, "I made mistakes and was not able to stop what should have been stopped. That, is my guilt!" He then went on to wish the Germans hope and a new future in the community of nations.[10]
To underscore the criminal rather than military nature of Keitel's acts, the Allies denied his request to be shot by firing squad. Instead, he was executed by hanging.[11] Keitel's last words were:
"I call on God Almighty to have mercy on the German people. More than 2 million German soldiers went to their death for the fatherland before me. I follow now my sons – all for Germany"[12]
The execution was performed by the experienced American Army hangman, Sgt. John C. Woods.[13][14][15]
The reason for the facial blood stains seen in the photo of Keitel's corpse were due to the trapdoor being too small, causing several of the condemned to suffer head injuries whilst hitting the trapdoor during the drop.[16]
Leadership and suicide
After defeat outside Moscow in December 1941, Keitel, like so many other generals, had to act as a scapegoat. In the following days he contemplated suicide. At the Nuremberg Trials in 1946, general Alfred Jodl said:
"In front of him on the desk lay his pistol, which I took away myself"[17]
When asked about his leadership, Count Johann Kielmansegg said:
"Good leadership can be judged by the size of the losses. The idea and aim of good leadership at the front, is to do everything with a mind to keeping the losses as small as possible. He didn't care about that"[17]
Service summary
Dates of rank
- Fähnrich (Ensign) – 14 October 1901
- Leutnant (Second Lieutenant) – 18 August 1902
- Oberleutnant (Lieutenant) – 18 August 1910
- Hauptmann (Captain) – 8 August 1914
- Major – 1 June 1923
- Oberstleutnant (Lieutenant-Colonel) – 1 February 1929
- Oberst (Colonel) – 1 October 1931
- Generalmajor (Brigadier-General) – 1 April 1934
- Generalleutnant (Major-General) – 1 January 1936
- General der Artillerie (General of Artillery (Lieutenant-General)) – 1 August 1937
- Generaloberst (Supreme General (General)) – 1 November 1938
- Generalfeldmarschall (Field Marshal) – 19 July 1940
Awards and decorations
- Knight's Cross
- Wound Badge
- Prussian Iron Cross, 1st and 2nd Class (1914)
- Clasp to the Iron Cross, 1st and 2nd Class (1939)
- Prussian Royal House Order of Hohenzollern, Knight's Cross with Swords
- Brunswick War Merit Cross, 1st Class and 2nd Class with "Bewährung" (Reliability) Clasp
- Ducal Saxe-Ernestine House Order, Knight 2nd Class with Swords
- Hesse General Honor Decoration, "for Bravery"
- Oldenburg Friedrich August Cross, 1st Class and 2nd Class with "Vor Dem Feinde" (In the Face of the Enemy) Clasp
- Hamburg Hanseatic Cross
- Bremen Hanseatic Cross
- Honour Cross of the World War 1914/1918
- Brunswick Ducal Order of Henry the Lion, 4th Class
- Wehrmacht Long Service Award, 1st Class (25-year Service Cross) and 3rd Class (12-year Service Medal)
- Austrian Military Merit Cross, 3rd Class with War Decoration
- Anschluss Medal of 13 March 1938
- Sudetenland Medal with Prague Castle Bar
- Memel Medal
Legacy
Wilhelm Keitel wrote his memoirs in the six weeks before he was hanged; they have been published later in few editions, for example "The Memoirs of Field-Marshal Wilhelm Keitel: Chief of the German High Command, 1938–1945" edited by Walter Görlitz, ISBN 978-0-8154-1072-0.
When moving to the United States and Australia after World War II, some of Keitel's family changed their surname to Kihtel, Keetle, Kaidel, Keidel, Keidle, and Feitel so as to not be associated with his legacy.
Film portrayals
Wilhelm Keitel has been portrayed by the following actors in film and television productions:
- Dieter Mann as Generalfeldmarschall Wilhelm Keitel in the 2004 German film Downfall (Der Untergang).
See also
Notes
- ↑ Wilhelm Keitel at ww2gravestone.com
- ↑ Bodewin Keitel at ww2gravestone.com
- ↑ www.youtube.com/watch?v=WfI-80yXOD8
- ↑ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2gZ3UcTIZ9o
- ↑ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ffGSbHM4o-Q
- ↑ Burleigh, Michael, Moral Combat, HarperPress, 2010, London, UK, ISBN 978-0-00-719576-3
- ↑ Historical Division, Headquarters, United States Army, Europe, Foreign Military Studies Branch (1949)
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Keitel judgement at Nuremberg".
- ↑ William Shirer, The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich (Touchstone Edition) (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1990)
- ↑ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jpsBg8H5_24
- ↑ "The Trial of the Century – and of all time". Part two. By Donald E. Wilkes, Jr., Professor of Law, University of Georgia School of Law.
- ↑ "Nuremberg Trials 60th Anniversary". Anti-Defamation League. 2006. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ↑ TIME Magazine, 28 October 1946, p. 34
- ↑ Kingsbury Smith: The Execution of Nazi War Criminals. Eyewitness Report.
- ↑ TURLEY, Mark. From Nuremberg to Nineveh
- ↑ Spiegel Online, Nürnberger Prozesse: Der Tod durch den Strick dauerte 15 Minuten (German), 16 January 2007
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N1B2idchILo
Bibliography
- Michael Burleigh, Moral Combat, HarperPress, 2010, London, UK, ISBN 978-0-00-719576-3
- Alan Clark, Barbarossa, Perennial, 2002. ISBN 0-688-04268-6
- Trumbull Higgins, Hitler and Russia. The Macmillan Company, 1966.
- Guido Knopp, Hitlers Krieger. Goldmann Verlag, 2000. ISBN 3-442-15045-0
- Douglas Brinkle and Michael E. Haskey, The World War II Desk Reference. Grand Central Press, 2004.
- Donald L. Miller, The Story of World War II. Simon & Schuster, 2006. ISBN 0-7432-2718-2.
- Gene Mueller, The Forgotten Field Marshal: Wilhelm Keitel. Moore Publ., 1979.
- Paul Carell, Scorched Earth. Schiffer Military History, 1994. ISBN 0-88740-598-3
External links
![]() Media related to Wilhelm Keitel at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Wilhelm Keitel at Wikimedia Commons
![]() Quotations related to Wilhelm Keitel at Wikiquote
Quotations related to Wilhelm Keitel at Wikiquote
- Wilhelm Keitel in the German National Library catalogue
| Awards and achievements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Yosuke Matsuoka |
Cover of Time Magazine 14 July 1941 |
Succeeded by Claude Wickard |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||
|

