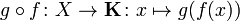Weakly measurable function
In mathematics — specifically, in functional analysis — a weakly measurable function taking values in a Banach space is a function whose composition with any element of the dual space is a measurable function in the usual (strong) sense. For separable spaces, the notions of weak and strong measurability agree.
Definition
If (X, Σ) is a measurable space and B is a Banach space over a field K (usually the real numbers R or complex numbers C), then f : X → B is said to be weakly measurable if, for every continuous linear functional g : B → K, the function
is a measurable function with respect to Σ and the usual Borel σ-algebra on K.
Properties
The relationship between measurability and weak measurability is given by the following result, known as Pettis' theorem or Pettis measurability theorem.
A function f is said to be almost surely separably valued (or essentially separably valued) if there exists a subset N ⊆ X with μ(N) = 0 such that f(X \ N) ⊆ B is separable.
Theorem (Pettis). A function f : X → B defined on a measure space (X, Σ, μ) and taking values in a Banach space B is (strongly) measurable (with respect to Σ and the Borel σ-algebra on B) if and only if it is both weakly measurable and almost surely separably valued.
In the case that B is separable, since any subset of a separable Banach space is itself separable, one can take N above to be empty, and it follows that the notions of weak and strong measurability agree when B is separable.
See also
- Bochner measurable function
- Bochner integral
- Pettis integral
- Vector-valued measure
References
- Showalter, Ralph E. (1997). "Theorem III.1.1". Monotone operators in Banach space and nonlinear partial differential equations. Mathematical Surveys and Monographs 49. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society. p. 103. ISBN 0-8218-0500-2. MR 1422252..