Waterfall chart

A waterfall chart is a form of data visualization that helps in determining the cumulative effect of sequentially introduced positive or negative values. The waterfall chart is also known as a flying bricks chart or Mario chart due to the apparent suspension of columns (bricks) in mid-air. Often in finance, it will be referred to as a bridge.
Waterfall charts were popularized by the strategic consulting firm McKinsey & Company in its presentations to clients.[1][2]
Overview
The waterfall chart is normally used for understanding how an initial value is affected by a series of intermediate positive or negative values. Usually the initial and the final values are represented by whole columns, while the intermediate values are denoted by floating columns. The columns are color-coded for distinguishing between positive and negative values.
Applications
A waterfall chart can be used for analytical purposes, especially for understanding or explaining the gradual transition in the quantitative value of an entity which is subjected to increment or decrement.
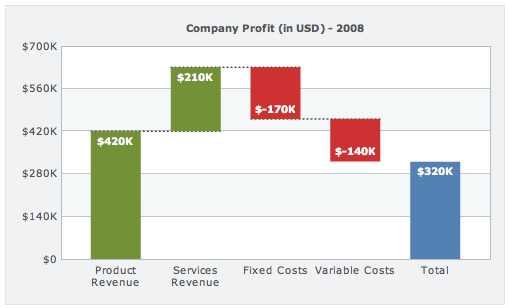
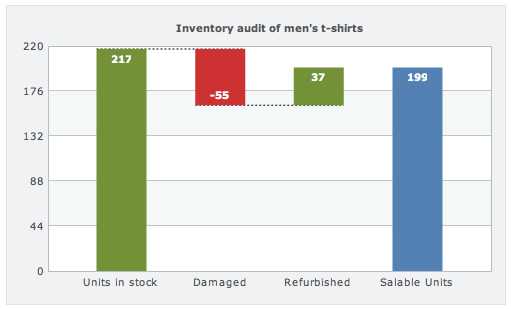
Waterfall charts can be used for various types of quantitative analysis, ranging from inventory analysis to performance analysis.
References
- ↑ "How to Create a McKinsey-style waterfall chart". Idea transplant.
- ↑ Ethan M. Rasiel. The McKinsey Way. McGraw–Hill, 1999.