Walker River
| Walker River | |
| River | |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| State | Nevada |
| Cities | Yerington, Mason, Wabuska |
| Primary source | West Walker River |
| - location | Sierra Nevada, California |
| - elevation | 9,640 ft (2,938 m) |
| - coordinates | 38°08′24″N 119°30′28″W / 38.14000°N 119.50778°W [1] |
| Secondary source | East Walker River |
| - location | Bridgeport Valley, California |
| - elevation | 6,570 ft (2,003 m) |
| - coordinates | 38°11′44″N 119°17′09″W / 38.19556°N 119.28583°W [2] |
| Source confluence | |
| - location | Yerington, Lyon County, Nevada |
| - elevation | 4,442 ft (1,354 m) |
| - coordinates | 38°53′35″N 119°10′44″W / 38.89306°N 119.17889°W [3] |
| Mouth | Walker Lake |
| - location | Mineral County, Nevada |
| - elevation | 3,973 ft (1,211 m) |
| - coordinates | 38°48′56″N 118°44′40″W / 38.81556°N 118.74444°W [3] |
| Length | 62 mi (100 km) |
| Basin | 3,134 sq mi (8,117 km2) |
| Discharge | for Wabuska, NV |
| - average | 164 cu ft/s (5 m3/s) |
| - max | 3,280 cu ft/s (93 m3/s) |
| - min | 0 cu ft/s (0 m3/s) |
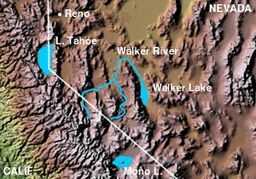 Walker River and Walker Lake
| |
The Walker River is a river in west central Nevada in the United States, approximately 62 miles (100 km) long. It drains an arid portion of the Great Basin southeast of Reno, with a watershed that extends into the Sierra Nevada mountains. It flows within an enclosed basin, providing the principal inflow of Walker Lake as well as Topaz Lake (West Fork). The river was named for explorer Joseph Reddeford Walker. Its average discharge is about 360 cubic feet per second (10 m3/s).
It is formed in southern Lyon County, 9 mi (11 km) south of Yerington, by the confluence of the East Walker and West Walker rivers, the East Walker is regulated by the Bridgeport Reservoir while the West Walker comes directly from snowmelt. It flows initially north past Yerington into central Lyon County, where it turns sharply to the southeast, flowing through the Walker River Indian Reservation past Schurz. It enters the northern end of Walker Lake, along the east side of the Wassuk Range, approximately 20 mi (32 km) NNW of Hawthorne.
Most of the streamflow is consumed by irrigation before reaching Walker Lake. The diversions have caused the level of Walker lake to drop by 140 ft (42 m) between 1882 and 1994. The eastern branch of the river is one of the last natural trout fisheries in California.
Due to a very heavy snowpack in the winter of 1996/1997 and a very warm spring the west fork of the Walker River flooded to unprecedented levels. Much of Highway 395 for the 30 mile span where it shares a canyon with the river was completely washed away.
Drainage Basin
The Walker River's endorheic drainage basin covers an area of 12,800 sq mi (33,000 km2).[4] The U.S. Geological Survey divides the basin into 4 sub-basins:
- West Walker of 992 sq mi (2,570 km2)[4]
- East Walker of 1,080 sq mi (2,800 km2)[4]
- Walker River of 1,010 sq mi (2,600 km2)[4]
- Walker Lake of 835 sq mi (2,160 km2)[4]
Ecology
That North American Beaver (Castor canadensis) were once native to the Walker River is evidenced by a 1906 article in the Nevada State Journal newspaper by newspaper mining writer Fitz-James MacCarthy (aka Fitz-Mac) stated that the Mason's Valley of the Walker River in Yerington, Nevada was well known to "the early trappers and fur hunters...Kit Carson knew it to the bone...The beavers of course were all trapped long ago, and you never see an elk nowadays..."[5]
See also
- List of Nevada rivers
- List of rivers in the Great Basin
References
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: West Walker River
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: East Walker River
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Walker River
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "Boundary Descriptions and Names of Regions, Subregions, Accounting Units and Cataloging Units". USGS.gov. Retrieved 2010-10-19.
- ↑ Fitz-James MacCarthy (1906-02-18). "Wonderful Deposits of High-Grade Rock". Nevada State Journal. Retrieved 2011-07-10.