Volemitol
| Volemitol | |
|---|---|
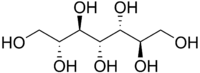 | |
| IUPAC name (2R,3R,5R,6R)-heptane-1,2,3,4,5,6,7-heptol | |
| Other names D-glycero-D-talo-heptitol, alpha-sedoheptitol, | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 488-38-0 |
| ChemSpider | 390172 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)C(O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)CO|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C7H16O7 |
| Molar mass | 212.20 g mol−1 |
| Melting point | 152-153 °C |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Volemitol is a naturally occurring seven-carbon sugar alcohol. It is a substance widely distributed in plants, red algae, fungi, mosses, and lichens. It was also found in lipopolysaccharides from E. coli. In certain higher plants, such as Primula, volemitol plays several important physiological roles. It functions as a photosynthetic product, phloem translocate, and storage carbohydrate.
It is used as a natural sweetening agent.
Volemitol was first isolated as a white crystalline substance from the mushroom Lactarius volemus by the French scientist Émile Bourquelot in 1889.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ E. Bourquelot, Bull. Soc. Mycol. Fr., 5 (1889) 132.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||