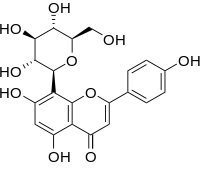
Vitexin
| Vitexin | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 3681-93-4 |
| PubChem | 5280441 |
| ChemSpider | 4444098 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16954 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL487417 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O=C2\C=C(/Oc1c(c(O)cc(O)c12)[C@@H]3O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]3O)CO)c4ccc(O)cc4|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C21H20O10 |
| Molar mass | 432.38 g/mol |
| Appearance | Light yellow powder |
| Melting point | 203–204 °C |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. |
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas |
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Vitexin is an apigenin flavone glucoside, a chemical coupound found in the passion flower, Vitex agnus-castus (chaste tree or chasteberry) and in the Phyllostachys nigra bamboo leaves.[1] It is also found in the pearl millet (Pennisetum millet).[2] Vitexin is also found in Hawthorn.[citation needed]
Metabolism
Goitrogenicity of millet flavones : Vitexin inhibits thyroid peroxidase thus contributing to goiter.[3][4]
See also
Isovitexin (or homovitexin, saponaretin) is the apigenin-6-C-glucoside.
References
- ↑ Zhang, Y; Jiao, J; Liu, C; Wu, X; Zhang, Y (2007). "Isolation and purification of four flavone C-glycosides from antioxidant of bamboo leaves by macroporous resin column chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography". Food Chemistry. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.09.037.
- ↑ J.O. AKINGBALA (1991). "Effect of Processing on Flavonoids in Millet (Pennisetum americanum) Flour". Cereal Chem. 68 (2): 180–183.
- ↑ Gaitan, E (1990). "Goitrogens in food and water.". Annual review of nutrition 10: 21–39. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.10.070190.000321. PMID 1696490.
- ↑ Birzer, D. M., Klopfenstein, C. F., Leipold, H. W. (1987). "Goitre causing compounds found in pearl millet". Nutr. Rep. Int. 36: 131.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||