Vitamin D-binding protein
| Group-specific component (vitamin D binding protein) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Crystallographic structure of the human vitamin D-binding protein.[1] | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | GC; DBP; DBP/GC; GRD3; VDBG; VDBP | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 139200 MGI: 95669 HomoloGene: 486 ChEMBL: 2259 GeneCards: GC Gene | ||||||||||||
| EC number | 6.4.-.- | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 2638 | 14473 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000145321 | ENSMUSG00000035540 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | P02774 | P21614 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_000583 | NM_008096 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_000574 | NP_032122 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 4: 72.61 – 72.67 Mb | Chr 5: 89.42 – 89.46 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
Vitamin D-binding protein, also known as gc-globulin (group-specific component), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GC gene.[2][3]
Function
Vitamin D-binding protein belongs to the albumin gene family, together with human serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein. It is a multifunctional protein found in plasma, ascitic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid and on the surface of many cell types. It binds to vitamin D and its plasma metabolites and transports them to target tissues.[3] As Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor it is a Macrophage Activating Factor (MAF) that has been tested for use as a cancer treatment that would activate macrophages against cancer cells.[4]
Structure
Human GC is a glycosylated alpha-globulin, ~58 kDa in size. Its 458 amino acids are coded for by 1690 nucleotides on chromosome 4 (4q11–q13). The primary structure contains 28 cysteine residues forming multiple disulfide bonds. GC contains 3 domains. Domain 1 is composed of 10 alpha helices, domain 2 of 9, and domain 3 of 4.[1]
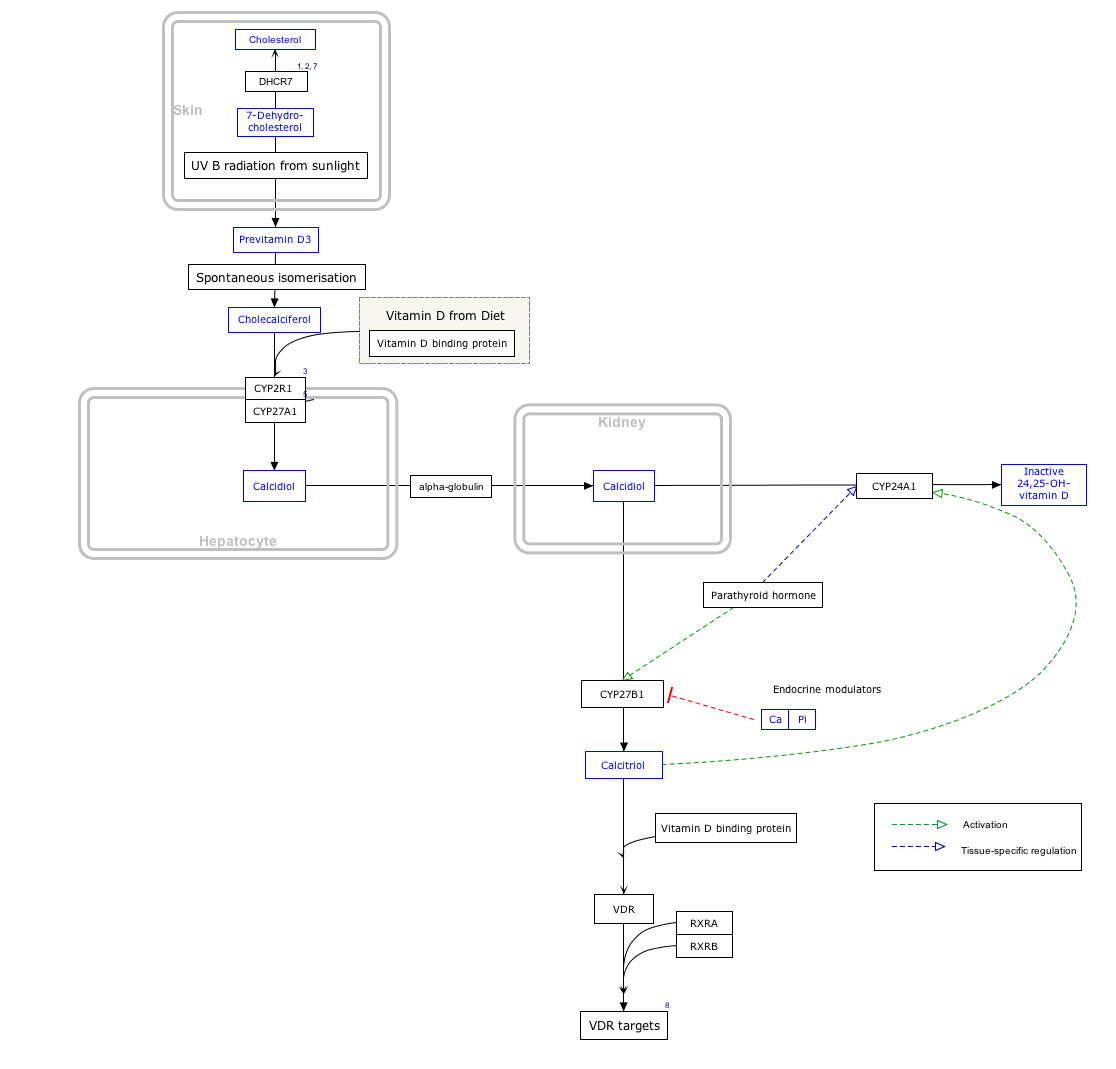
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ↑ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 PDB 1J78; Verboven C, Rabijns A, De Maeyer M, Van Baelen H, Bouillon R, De Ranter C (February 2002). "A structural basis for the unique binding features of the human vitamin D-binding protein". Nat. Struct. Biol. 9 (2): 131–6. doi:10.1038/nsb754. PMID 11799400.
- ↑ Mikkelsen M, Jacobsen P, Henningsen K (Jul 1977). "Possible localization of Gc-System on chromosome 4. Loss of long arm 4 material associated with father-child incompatibility within the Gc-System". Hum Hered 27 (2): 105–7. PMID 558959.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Entrez Gene: GC group-specific component (vitamin D binding protein)".
- ↑ Yamamoto N, Suyama H, Yamamoto N (2008). "Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer with Gc Protein-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor, GcMAF" ([PDF]). TRANSLATIONAL ONCOLOGY 1 (2): 65–72. PMC 2510818. PMID 18633461.
Further reading
- Svasti J, Kurosky A, Bennett A, Bowman BH (1979). "Molecular basis for the three major forms of human serum vitamin D binding protein (group-specific component).". Biochemistry 18 (8): 1611–7. doi:10.1021/bi00575a036. PMID 218624.
- Braun A, Bichlmaier R, Cleve H (1992). "Molecular analysis of the gene for the human vitamin-D-binding protein (group-specific component): allelic differences of the common genetic GC types.". Hum. Genet. 89 (4): 401–6. doi:10.1007/BF00194311. PMID 1352271.
- Esteban C, Geuskens M, Ena JM, et al. (1992). "Receptor-mediated uptake and processing of vitamin D-binding protein in human B-lymphoid cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (14): 10177–83. PMID 1374401.
- Szpirer C, Riviere M, Cortese R, et al. (1992). "Chromosomal localization in man and rat of the genes encoding the liver-enriched transcription factors C/EBP, DBP, and HNF1/LFB-1 (CEBP, DBP, and transcription factor 1, TCF1, respectively) and of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor gene (HGF).". Genomics 13 (2): 293–300. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90245-N. PMID 1535333.
- Dawson SJ, White LA (1992). "Treatment of Haemophilus aphrophilus endocarditis with ciprofloxacin.". J. Infect. 24 (3): 317–20. doi:10.1016/S0163-4453(05)80037-4. PMID 1602151.
- Yang F, Bergeron JM, Linehan LA, et al. (1990). "Mapping and conservation of the group-specific component gene in mouse.". Genomics 7 (4): 509–16. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(90)90193-X. PMID 1696927.
- Yang F, Luna VJ, McAnelly RD, et al. (1986). "Evolutionary and structural relationships among the group-specific component, albumin and alpha-fetoprotein.". Nucleic Acids Res. 13 (22): 8007–17. doi:10.1093/nar/13.22.8007. PMID 2415926.
- Yang F, Brune JL, Naylor SL, et al. (1986). "Human group-specific component (Gc) is a member of the albumin family.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82 (23): 7994–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.23.7994. PMID 2415977.
- Cooke NE, David EV (1986). "Serum vitamin D-binding protein is a third member of the albumin and alpha fetoprotein gene family.". J. Clin. Invest. 76 (6): 2420–4. doi:10.1172/JCI112256. PMID 2416779.
- Schoentgen F, Metz-Boutigue MH, Jollès J, et al. (1986). "Complete amino acid sequence of human vitamin D-binding protein (group-specific component): evidence of a three-fold internal homology as in serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 871 (2): 189–98. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(86)90173-1. PMID 2423133.
- McNearney TA, Odell C, Holers VM, et al. (1987). "Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gC-1 and gC-2 bind to the third component of complement and provide protection against complement-mediated neutralization of viral infectivity.". J. Exp. Med. 166 (5): 1525–35. doi:10.1084/jem.166.5.1525. PMID 2824652.
- Yang F, Naberhaus KH, Adrian GS, et al. (1987). "The vitamin D-binding protein gene contains conserved nucleotide sequences that respond to heavy metal, adipocyte and mitotic signals.". Gene 54 (2-3): 285–90. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(87)90499-9. PMID 2958390.
- Cooke NE, Willard HF, David EV, George DL (1986). "Direct regional assignment of the gene for vitamin D binding protein (Gc-globulin) to human chromosome 4q11-q13 and identification of an associated DNA polymorphism.". Hum. Genet. 73 (3): 225–9. doi:10.1007/BF00401232. PMID 3015768.
- Nestler JE, McLeod JF, Kowalski MA, et al. (1987). "Detection of vitamin D binding protein on the surface of cytotrophoblasts isolated from human placentae.". Endocrinology 120 (5): 1996–2002. doi:10.1210/endo-120-5-1996. PMID 3552627.
- Pierce EA, Dame MC, Bouillon R, et al. (1986). "Monoclonal antibodies to human vitamin D-binding protein.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82 (24): 8429–33. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.24.8429. PMID 3936035.
- Wooten MW, Nel AE, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, et al. (1985). "Identification of a major endogenous substrate for phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent kinase in pancreatic acini as Gc (vitamin D-binding protein).". FEBS Lett. 191 (1): 97–101. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(85)81001-2. PMID 4054306.
- Constans J, Oksman F, Viau M (1981). "Binding of the apo and holo forms of the serum vitamin D-binding protein to human lymphocyte cytoplasm and membrane by indirect immunofluorescence.". Immunol. Lett. 3 (3): 159–62. doi:10.1016/0165-2478(81)90120-6. PMID 7026425.
- Braun A, Kofler A, Morawietz S, Cleve H (1994). "Sequence and organization of the human vitamin D-binding protein gene.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1216 (3): 385–94. PMID 7505619.
- Swamy N, Roy A, Chang R, et al. (1995). "Affinity purification of human plasma vitamin D-binding protein.". Protein Expr. Purif. 6 (2): 185–8. doi:10.1006/prep.1995.1023. PMID 7606167.
| ||||||||||||||||||