Visual artifact
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Visual artifacts are anomalies during visual representation of e.g. digital graphics and imagery.
Examples in digital graphics
A screenshot of a Microsoft Windows XP application displaying a visual artifact. This was fixed in the next release, Windows Vista [citation needed].
- Image quality factors, different types of visual artifacts
- Digital artifacts, visual artifacts resulting from digital image processing
- Noise
- Screen-door effect, also known as fixed-pattern noise (FPN), a visual artifact of digital projection technology
- Distortion
- Silk screen effect
- Rainbow effect
- Screen tearing
- Purple fringing
- Chromatic aberration
- Moiré pattern
- Color banding
Occurrences in video entertainment
Many people who use their computers as a hobby experience artifacting due to a hardware malfunction. The cases can differ but the usual causes are:
- Fan issues, such as failure of cooling fan.
- Unsuited video card drivers.
- Drivers that have values that the graphics card is not suited with.
- Overclocking beyond the capabilities of the particular video card.
The differing cases of visual artifacting can also differ between scheduled task(s).
In microscopy
In microscopy, an artifact is an apparent structural detail that is caused by the processing of the specimen and is thus not a legitimate feature of the specimen.
For example, a crush artifact is artificial elongation and distortion when smearing cells or tissue for microscopy.[1]
References
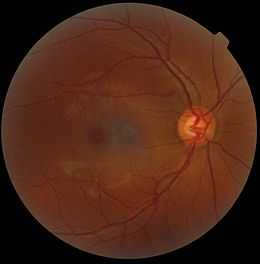
A retinography. The gray spot in the center is a shadow artifact.
- ↑ Komanduri S, Swanson G, Keefer L, Jakate S (December 2009). "Use of a new jumbo forceps improves tissue acquisition of Barrett's esophagus surveillance biopsies". Gastrointest. Endosc. 70 (6): 1072–8.e1. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2009.04.009. PMID 19595312.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.