Vildagliptin
 | |
|---|---|
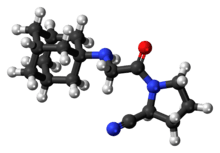 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (S)-1-[N-(3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl)glycyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Licence data | EMA:Link |
| Pregnancy cat. | Not recommended |
| Legal status | POM (UK) |
| Routes | Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 85% |
| Protein binding | 9.3% |
| Metabolism | Mainly hydrolysis to inactive metabolite; CYP450 not appreciably involved |
| Half-life | 2 to 3 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 274901-16-5 |
| ATC code | A10BH02 A10BD08 (with metformin)[1] |
| PubChem | CID 6918537 |
| DrugBank | DB04876 |
| ChemSpider | 5293734 |
| UNII | I6B4B2U96P |
| KEGG | D07080 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL142703 |
| Synonyms | (2S)-1-{2-[(3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl)amino]acetyl}pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C17H25N3O2 |
| Mol. mass | 303.399 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
'Vildagliptin (previously identified as LAF237, trade names Galvus, Zomelis) is an oral anti-hyperglycemic agent (anti-diabetic drug) of the new dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class of drugs. Vildagliptin inhibits the inactivation of GLP-1[2][3] and GIP[3] by DPP-4, allowing GLP-1 and GIP to potentiate the secretion of insulin in the beta cells and suppress glucagon release by the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.
Vildagliptin has been shown to reduce hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus.[2]
Combination with metformin
The EMEA has also approved a new oral treatment released by Novartis, called Eucreas, a combination of vildagliptin and metformin.[4]
Cancer risk of DPP-4 inhibitors
The DPP-4 enzyme is known to be involved in the suppression of certain malignancies, particularly in limiting the tissue invasion of these tumours. Inhibiting the DPP-4 enzymes may allow some cancers to progress.[5][6] A study of DPP-4 inhibition in human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) concluded that "DPPIV functions as a tumor suppressor, and its downregulation may contribute to the loss of growth control in NSCLC cells.[7]
The risk of cancer suppression with DPP-4 down-regulation applies to all the DPP-4 inhibitors on the market in addition to vildagliptin (sitagliptin and saxagliptin)
Synthetic Chemistry
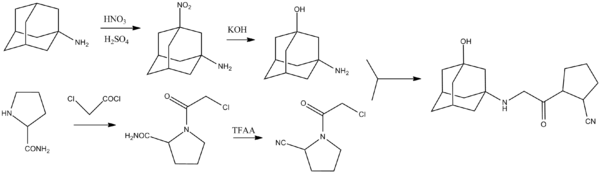
Source: 1-[[(3-Hydroxy-1-adamantyl)amino]acetyl]-2-cyano-(S)-pyrrolidine: A Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor with Antihyperglycemic Properties[8]
See also
References
- ↑ WHO International Working Group for Drug Statistics Methodology (August 27, 2008). "ATC/DDD Classification (FINAL): New ATC 5th level codes". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Retrieved 2008-09-05.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Ahrén, B; Landin-Olsson, M; Jansson, PA; Svensson, M; Holmes, D; Schweizer, A (2004). "Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 reduces glycemia, sustains insulin levels, and reduces glucagon levels in type 2 diabetes". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 89 (5): 2078–84. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031907. PMID 15126524.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mentlein, R; Gallwitz, B; Schmidt, WE (1993). "Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV hydrolyses gastric inhibitory polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36)amide, peptide histidine methionine and is responsible for their degradation in human serum". European journal of biochemistry / FEBS 214 (3): 829–35. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17986.x. PMID 8100523.
- ↑ EU approves Novartis's Eucreas diabetes drug. Reuters, February 25, 2008.
- ↑ Pro B, Dang NH (October 2004). "CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its role in cancer". Histol. Histopathol. 19 (4): 1345–51. PMID 15375776.
- ↑ Wesley UV, McGroarty M, Homoyouni A (February 2005). "Dipeptidyl peptidase inhibits malignant phenotype of prostate cancer cells by blocking basic fibroblast growth factor signaling pathway". Cancer Res. 65 (4): 1325–34. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1852. PMID 15735018.
- ↑ Wesley, U; et al (2004). "Role for dipeptidyl peptidase IV in tumor suppression of human non small cell lung carcinoma cells.". Int J Cancer 109 (6): 855–866. doi:10.1002/ijc.20091. PMID 15027119.
- ↑ Villhauer, Edwin B.; Brinkman, John A.; Naderi, Goli B.; Burkey, Bryan F.; Dunning, Beth E.; Prasad, Kapa; Mangold, Bonnie L.; Russell, Mary E. et al. (2003). "1-(3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl)aminoacetyl-2-cyano-(S)-pyrrolidine: a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor with antihyperglycemic properties.". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46 (13): 2774–89. doi:10.1021/jm030091l. PMID 12801240.
External links
- Banting and Best Diabetes Centre at UT vildagliptin – Vildagliptin
- Banting and Best Diabetes Centre at UT dpp4 – About DPP-4
- The race to get DPP-4 inhibitors to market – Forbes.com
- Merck's March Madness – Forbes.com
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||