Value (mathematics)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematics, value may refer to several, strongly related notions:
- A value of a variable or a constant is any number or other mathematical object assigned to it.
- A value of a mathematical expression is the result of the computation described by this expression when the variables and constants in it are replaced by some values.
- A value of a function is the result associated to a value of its argument (also called variable of the function).[1][2]
For example, if the function  is defined by
is defined by 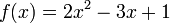 , then, given the value 3 to the variable x yields the function value 10 (since indeed 2 · 32 – 3 · 3 + 1 = 10). This is denoted
, then, given the value 3 to the variable x yields the function value 10 (since indeed 2 · 32 – 3 · 3 + 1 = 10). This is denoted 
References
- ↑ http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Value.html
- ↑ Meschkowski, Herbert (1968). Introduction to Modern Mathematics. George G. Harrap & Co. Ltd. p. 32. ISBN 0245591095.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.