Vaginal artery
| Artery: Vaginal artery | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Arteries of the female reproductive tract (posterior view): uterine artery, ovarian artery and vaginal arteries. | |
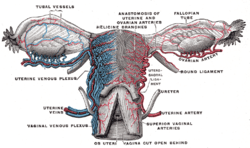 | |
| Vessels of the uterus and its appendages, rear view. | |
| Latin | arteria vaginalis |
| Gray's | p.616 |
| Supplies | urinary bladder, ureter, vagina |
| Source | Internal iliac artery Uterine artery |
| Vein | vaginal venous plexus |
The vaginal artery is an artery in females that supplies blood to the vagina and the base of the bladder.
Terminology
The vaginal artery is usually defined as a branch of the internal iliac artery.

Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the internal iliac artery or the uterine artery.[1] However, the phrase vaginal branches of uterine artery is the Terminologia Anatomica term for blood supply to the vagina coming from the uterine artery.
Some texts consider the inferior vesical artery to be found only in males, and that this structure in females is a vaginal artery.
Structure
It descends to the vagina, supplying its mucous membrane. It can send branches to the bulb of the vestibule, the fundus of the bladder, and the contiguous part of the rectum.
The vaginal artery is frequently represented by two or three branches.
See also
References
External links
- Vaginal+artery at eMedicine Dictionary
- 43:13-0206 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: Branches of Internal Iliac Artery"
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||