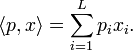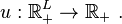Utility maximization problem
In microeconomics, the utility maximization problem is the problem consumers face: "how should I spend my money in order to maximize my utility?" It is a type of optimal decision problem.
Basic setup
Suppose their consumption set, or the enumeration of all possible consumption bundles that could be selected if there are no budget constraints, has L commodities and is limited to positive amounts of consumption of each commodity. Let x be the vector x={xi;i=1,...L} containing the amounts of each commodity, then
Suppose also that the prices (p) of the L commodities are positive
and that the consumer's wealth is w, then the set of all affordable packages, the budget set, is
where 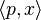 is the dot product of p and x, or the total cost of consuming x of the products at price level p:
is the dot product of p and x, or the total cost of consuming x of the products at price level p:
The consumer would like to buy the best package of commodities it can afford. Suppose that the consumer's utility function (u) is a real valued function with domain of the commodity bundles, or
Then the consumer's optimal choices x(p, w) are the utility maximizing bundle that is in the budget set, or
 .
.
Finding x(p, w) is the utility maximization problem. If u is continuous and no commodities are free of charge, then x(p, w) exists.[citation needed] If there is always a unique maximizer, then it is called the Marshallian demand function. The relationship between the utility function and Marshallian demand in the Utility Maximization Problem mirrors the relationship between the expenditure function and Hicksian demand in the Expenditure Minimization Problem.
In practice, a consumer may not always pick an optimal package. For example, it may require too much thought. Bounded rationality is a theory that explains this behaviour with satisficing - picking packages that are suboptimal but good enough.
Nonunique solution
The solution x(p, w) need not be unique.[citation needed] If a consumer always picks an optimal package as defined above, then x(p, w) is called the Marshallian demand correspondence.
See also
- Optimal decision
- Choice Modelling
- Utility function
- Expenditure minimization problem
- Profit maximization formulae
References
- Mas-Colell, Andreu; Whinston, Michael; & Green, Jerry (1995). Microeconomic Theory. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-507340-1.