Uterine artery
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Artery: Uterine artery | |
|---|---|
 | |
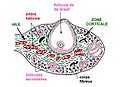
| Arteries of the female reproductive tract: uterine artery, ovarian artery and vaginal arteries. (Uterine artery labeled at center.) | |
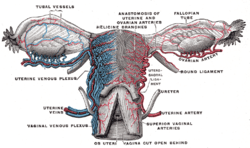 | |
| Vessels of the uterus and its appendages, rear view. (Uterine artery labeled at center right.) | |
| Latin | arteria uterina |
| Gray's | p.615 |
| Supplies | round ligament of the uterus, ovary, uterus, vagina, uterine tube |
| Source | internal iliac artery (i.e. hypogastric artery) |
| Vein | uterine veins |
The uterine artery is an artery that supplies blood to the uterus in females.
Structure
The uterine artery usually arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It travels to the uterus, crossing the ureter anteriorly, reaching the uterus by traveling in the cardinal ligament.

Uterine artery
It travels through the parametrium of the inferior broad ligament of the uterus.
It commonly anastomoses (connects with) the ovarian artery.
The uterine artery is the major blood supply to the uterus and enlarges significantly during pregnancy.
Branches and organs supplied
- round ligament of the uterus
- ovary ("Ovarian branches")
- uterus (arcuate vessels)
- vagina ("Vaginal branches" - azygos arteries of the vagina)
- uterine tube ("Tubal branch")
Additional images
See also
- Uterine artery embolization
- Uterine leiomyomata (fibroids of the uterus)
External links
- 43:13-0204 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: Branches of Internal Iliac Artery"
- Uterine+artery at eMedicine Dictionary
- pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (uterus)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.