Urogenital triangle
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Urogenital triangle | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Muscles of the female perineum. (Urogenital triangle is roughly equal to top half of diagram.) | |
 | |
| Muscles of male perineum. (Urogenital triangle is roughly equal to top half of diagram.) | |
| Latin | regio urogenitalis |
The urogenital triangle is the anterior part of the perineum. In female mammals, it contains the vagina and associated parts of the external genitalia.
Structure
The urogenital triangle is the area bound by a triangle with one vertex at the pubic symphysis and the two other vertices at the ischiopubic rami of the pelvic bone.
Components
As might be expected, the contents of the urogenital triangle differ greatly between the male and the female. Some of the components include:[1]
- Posterior scrotal nerves / Posterior labial nerves
- Urethra
- Vagina
- Bulbourethral gland / Bartholin's gland
- Muscles
- Transversus perinei superficialis muscle
- Ischiocavernosus muscle
- Bulbospongiosus muscle
- Crus penis / Clitoral crura
- Bulb of penis / vestibular bulb
- Urogenital diaphragm
- Muscular perineal body
- Superficial and Deep perineal pouch
- Blood vessels and lymphatics
Additional images
-
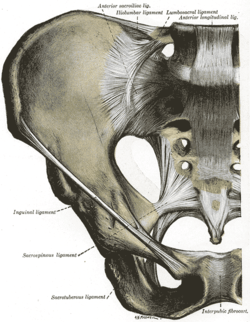
Articulations of pelvis. Anterior view.
-

The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery.
-

The posterior aspect of the rectum exposed by removing the lower part of the sacrum and the coccyx.
See also
References
- ↑ Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. ISBN 9788131225561.
External links
- 41:01-0201 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Perineum: Boundaries of the Female Perineum"
- perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (perineumboundaries)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.