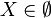Urelement
In set theory, a branch of mathematics, an urelement or ur-element (from the German prefix ur-, 'primordial') is an object (concrete or abstract) that is not a set, but that may be an element of a set. Urelements are sometimes called "atoms" or "individuals."
Theory
There are several different but essentially equivalent ways to treat urelements in a first-order theory.
One way is to work in a first-order theory with two sorts, sets and urelements, with a ∈ b only defined when b is a set. In this case, if U is an urelement, it makes no sense to say
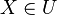 ,
,
although
 ,
,
is perfectly legitimate.
This should not be confused with the empty set where saying
is well-formed but false.
Another way is to work in a one-sorted theory with a unary relation used to distinguish sets and urelements. As non-empty sets contain members while urelements do not, the unary relation is only needed to distinguish the empty set from urelements. Note that in this case, the axiom of extensionality must be formulated to apply only to objects that are not urelements.
This situation is analogous to the treatments of theories of sets and classes. Indeed, urelements are in some sense dual to proper classes: urelements cannot have members whereas proper classes cannot be members. Put differently, urelements are minimal objects while proper classes are maximal objects by the membership relation (which, of course, is not an order relation, so this analogy is not to be taken literally.)
Urelements in set theory
The Zermelo set theory of 1908 included urelements. It was soon realized that in the context of this and closely related axiomatic set theories, the urelements were not needed because they can easily be modeled in a set theory without urelements. Thus standard expositions of the canonical axiomatic set theories ZF and ZFC do not mention urelements. (For an exception, see Suppes.[1]) Axiomatizations of set theory that do invoke urelements include Kripke–Platek set theory with urelements, and the variant of Von Neumann–Bernays–Gödel set theory described by Mendelson.[2] In type theory, an object of type 0 can be called an urelement; hence the name "atom."
Adding urelements to the system New Foundations (NF) to produce NFU has surprising consequences. In particular, Jensen proved[3] the consistency of NFU relative to Peano arithmetic; meanwhile, the consistency of NF relative to anything remains an open problem. Moreover, NFU remains relatively consistent when augmented with an axiom of infinity and the axiom of choice. Meanwhile, the negation of the axiom of choice is, curiously, an NF theorem. Holmes (1998) takes these facts as evidence that NFU is a more successful foundation for mathematics than NF. Holmes further argues that set theory is more natural with than without urelements, since we may take as urelements the objects of any theory or of the physical universe.[4]
Quine atoms
An alternative approach to urelements is to consider them, instead of as a type of object other than sets, as a particular type of set. Quine atoms are sets that only contain themselves, that is, sets that satisfy the formula x = {x}.[5]
Quine atoms cannot exist in systems of set theory that include the axiom of regularity, but they can exist in non-well-founded set theory. ZF set theory with the axiom of regularity removed is compatible with the existence of Quine atoms, although it does not prove that any non-well-founded sets exist. Aczel's anti-foundation axiom implies there is a unique Quine atom. Other non-well-founded theories may admit many distinct Quine atoms; at the opposite end of the spectrum lies Boffa's axiom of superuniversality, which implies that the distinct Quine atoms form a proper class.[6]
Quine atoms also appear in Quine's New Foundations, which allows more than one such set to exist.[7]
Quine atoms are the only sets called reflexive sets by Aczel,[6] although other authors, e.g. Jon Barwise and Lawrence Moss use the latter term to denote the larger class of sets with the property x ∈ x.[8]
References
- ↑ Suppes, Patrick (1972). Axiomatic Set Theory ([Éd. corr. et augm. du texte paru en 1960]. ed.). New York: Dover Publ. ISBN 0486616304. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ Mendelson, Elliott (1997). Introduction to Mathematical Logic (4th ed. ed.). London: Chapman & Hall. pp. 297–304. ISBN 978-0412808302. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ Jensen, Ronald Björn (December 1968). "On the Consistency of a Slight (?) Modification of Quine's 'New Foundations'". Synthese (Springer) 19 (1/2): 250–264. ISSN 0039-7857. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ Holmes, Randall, 1998. Elementary Set Theory with a Universal Set. Academia-Bruylant.
- ↑ Thomas Forster (2003). Logic, Induction and Sets. Cambridge University Press. p. 199. ISBN 978-0-521-53361-4.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Aczel, Peter (1988), Non-well-founded sets, CSLI Lecture Notes 14, Stanford University, Center for the Study of Language and Information, p. 57, ISBN 0-937073-22-9, MR 0940014
- ↑ Barwise, Jon; Moss, Lawrence S. (1996), Vicious circles. On the mathematics of non-wellfounded phenomena, CSLI Lecture Notes 60, CSLI Publications, p. 306, ISBN 1575860090
- ↑ Barwise, Jon; Moss, Lawrence S. (1996), Vicious circles. On the mathematics of non-wellfounded phenomena, CSLI Lecture Notes 60, CSLI Publications, p. 57, ISBN 1575860090