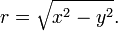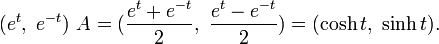Unit hyperbola

In geometry, the unit hyperbola is the set of points (x,y) in the Cartesian plane that satisfies 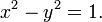 In the study of indefinite orthogonal groups, the unit hyperbola forms the basis for an alternative radial length
In the study of indefinite orthogonal groups, the unit hyperbola forms the basis for an alternative radial length
Whereas the unit circle surrounds its center, the unit hyperbola requires the conjugate hyperbola 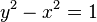 to complement it in the plane. This pair of hyperbolas share the asymptotes y = x and y = −x. When the conjugate of the unit hyperbola is in use, the alternative radial length is
to complement it in the plane. This pair of hyperbolas share the asymptotes y = x and y = −x. When the conjugate of the unit hyperbola is in use, the alternative radial length is 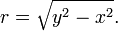
The unit hyperbola is a special case of the rectangular hyperbola, with a particular orientation, location, and scale. As such, its eccentricity equals 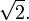
The unit hyperbola finds applications where the circle must be replaced with the hyperbola for purposes of analytic geometry. A prominent instance is the depiction of spacetime as a pseudo-Euclidean space. There the asymptotes of the unit hyperbola form a light cone. Further, the attention to areas of hyperbolic sectors by Gregoire de Saint-Vincent led to the logarithm function and the modern parametrization of the hyperbola by sector areas. When the notions of conjugate hyperbolas and hyperbolic angles are understood, then the classical complex numbers, which are built around the unit circle, can be replaced with numbers built around the unit hyperbola.
Asymptotes
Generally asymptotic lines to a curve are said to converge toward the curve. In algebraic geometry and the theory of algebraic curves there is a different approach to asymptotes. The curve is first interpreted in the projective plane using homogeneous coordinates. Then the asymptotes are lines that are tangent to the projective curve at a point at infinity, thus circumventing any need for a distance concept and convergence. In a common framework (x, y, z) are homogeneous coordinates with the line at infinity determined by the equation z = 0. For instance, C. G. Gibson wrote:[1]
- For the standard rectangular hyperbola
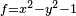 in R2 the corresponding projective curve is
in R2 the corresponding projective curve is  which meets z = 0 at the points P = (1 : 1 : 0) and Q = (1 : −1 : 0). Both P, Q are simple on F, with tangents x + y = 0, x − y = 0; thus we recover the familiar 'asymptotes' of elementary geometry.
which meets z = 0 at the points P = (1 : 1 : 0) and Q = (1 : −1 : 0). Both P, Q are simple on F, with tangents x + y = 0, x − y = 0; thus we recover the familiar 'asymptotes' of elementary geometry.
Minkowski diagram
The Minkowski diagram is drawn in a spacetime plane where the spatial aspect has been restricted to a single dimension. The units of distance and time on such a plane are
- units of 30 centimetres length and nanoseconds, or
- astronomical units and intervals of 8 minutes and 20 seconds, or
- light years and years.
Each of these scales of coordinates results in photon connections of events along diagonal lines of slope plus or minus one.
Five elements constitute the diagram Hermann Minkowski used to describe the relativity transformations: the unit hyperbola, its conjugate hyperbola, the axes of the hyperbola, a diameter of the unit hyperbola, and the conjugate diameter.
The plane with the axes refers to a resting frame of reference. The diameter of the unit hyperbola represents a frame of reference in motion with rapidity a where 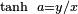 and (x,y) is the endpoint of the diameter on the unit hyperbola. The conjugate diameter represents the spatial hyperplane of simultaneity corresponding to rapidity a.
In this context the unit hyperbola is a calibration hyperbola[2][3]
and (x,y) is the endpoint of the diameter on the unit hyperbola. The conjugate diameter represents the spatial hyperplane of simultaneity corresponding to rapidity a.
In this context the unit hyperbola is a calibration hyperbola[2][3]
Commonly in relativity study the hyperbola with vertical axis is taken as primary:
- The arrow of time goes from the bottom to top of the figure — a convention adopted by Richard Feynman in his famous dagrams. Space is represented by planes perpendicular to the time axis. The here and now is a singularity in the middle.[4]
The vertical time axis convention stems from Minkowski in 1908, and is also illustrated on page 48 of Eddington's The Nature of the Physical World (1928).
Parametrization
As a particular conic, the hyperbola can be parametrized by the process of addition of points on a conic. The following description was given by Russian analysts:
- Fix a point E on the conic. Consider the points at which the straight line drawn through E parallel to AB intersects the conic a second time to be the sum of the points A and B.
- For the hyperbola
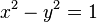 with the fixed point E = (1,0) the sum of the points
with the fixed point E = (1,0) the sum of the points  and
and 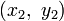 is the point
is the point 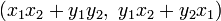 under the parametrization
under the parametrization  and
and 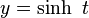 this addition corresponds to the addition of the parameter t.[5]
this addition corresponds to the addition of the parameter t.[5]

This parameter is hyperbolic angle, which is the argument of the hyperbolic functions.
One finds an early expression of the parametrized unit hyperbola in Elements of Dynamic (1878) by W. K. Clifford. He describes quasi-harmonic motion in a hyperbola as follows:
- The motion
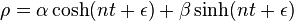 has some curious analogies to elliptic harmonic motion. ... The acceleration
has some curious analogies to elliptic harmonic motion. ... The acceleration  thus it is always proportional to the distance from the centre, as in elliptic harmonic motion, but directed away from the centre.[6]
thus it is always proportional to the distance from the centre, as in elliptic harmonic motion, but directed away from the centre.[6]
A direct way to parameterizing the unit hyperbola starts with the hyperbola xy = 1 parameterized with the exponential function: 
This hyperbola is transformed into the unit hyperbola by a linear mapping having the matrix 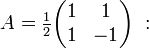
Complex plane algebra
Whereas the unit circle is associated with complex numbers, the unit hyperbola is key to the split-complex number plane consisting of z = x + y j where j 2 = +1. Then jz = y + x j so that the action of j on the plane is to swap the coordinates. In particular, this action swaps the unit hyperbola with its conjugate, and also swaps pairs of conjugate diameters of the hyperbolas.
In terms of the hyperbolic angle parameter a, the unit hyperbola consists of points
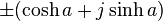 where j = (0,1).
where j = (0,1).
The right branch of the unit hyperbola corresponds to the positive coefficient. In fact, this branch is the image of the exponential map acting on the j-axis. Since
the branch is a group under multiplication. Unlike the circle group, this unit hyperbola group is not compact. Similar to the ordinary complex plane, a point, not on the diagonals, has a polar decomposition using the parametrization of the unit hyperbola and the alternative radial length.
References
- ↑ C.G. Gibson (1998) Elementary Geometry of Algebraic Curves, p 159, Cambridge University Press ISBN 0-521-64140-3
- ↑ Anthony French (1968) Special Relativity, page 83, W. W. Norton & Company
- ↑ W.G.V. Rosser (1964) Introduction to the Theory of Relativity, figure 6.4, page 256, London: Butterworths
- ↑ A.P. French (1989) "Learning from the past; Looking to the future", acceptance speech for 1989 Oersted Medal, American Journal of Physics 57(7):587–92
- ↑ Viktor Prasolov & Yuri Solovyev (1997) Elliptic Functions and Elliptic Integrals, page one, Translations of Mathematical Monographs volume 170, American Mathematical Society
- ↑ William Kingdon Clifford (1878) Elements of Dynamic, pages 89 & 90, London: MacMillan & Co; on-line presentation by Cornell University Historical Mathematical Monographs
- F. Reese Harvey (1990) Spinors and calibrations, Figure 4.33, page 70, Academic Press, ISBN 0-12-329650-1 .