Unhappy triad
| Unhappy triad | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
 Knee | |
| ICD-10 | S83.7 |
| MedlinePlus | 001074 |
An unhappy triad (or terrible triad, "horrible triangle", O'Donoghue's triad[1] or a "blown knee") is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and the meniscus. The triad refers to a complete or partial tear of the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and the meniscus. Originally the "unhappy triad" included the medial meniscus and not the lateral meniscus. However, during the 1990s, analysis indicated that the 'classic' O'Donoghue triad is actually an unusual clinical entity among athletes with knee injuries. In this type of injury, acute tears of the medial meniscus always present with a concomitant lateral meniscus injury. However, the lateral meniscus tears are far more common than medial meniscus tears in sprains of the ACL.
History
In 1936 Cambell stated that an "impairment of the anterior crucial and medial ligaments is associated with injuries of the internal cartilage". In 1950, O'Donoghue described the unhappy triad as: (1) rupture of the medial collateral ligament, (2) damage to the medial meniscus and (3) rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament. O'Donoghue estimated the incidence rate in the traumatic sports knee to be 25%.[2]
In 1991, Shelbourne and Nitz questioned the validity of O'Donoghue's terrible triad study. A review of all arthroscopically confirmed acute injuries of second degree or worse to the ACL and MCL was performed. Of the 52 knees reviewed, 80% of group 1 had lateral meniscus tears and 29% had associated medial meniscus tears. None of the medial meniscus tears were isolated; medial meniscus tears were not present in the absence of a lateral meniscus tear.[2] From this study, it was concluded that the structures involved in the terrible triad were the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and the lateral (not medial) meniscus.
Skeletal and Muscle Elements Involved
Skeletal components involved in the unhappy triad include:
No muscles are directly involved in this injury, only ligaments; However, strengthening the hip flexor and hip extensor muscles may help alleviate the injury.
The medial collateral ligament, posterior cruciate ligament, anterior cruciate ligament, and lateral collateral ligament are the four primary ligaments of the knee. The medial and lateral collateral ligaments primarily provide support to varus and valgus forces whereas the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments prevent anterior and posterior translation of the tibia on the femur.[3]
Structures in triad
The classic O'Donoghue triad is characterized by an injury to three knee structures:
- the anterior cruciate ligament
- the medial collateral ligament (or "tibial collateral ligament")
- the medial meniscus (however, lateral meniscus[1] injuries are more commonly seen among athletes, leading to the definition of the O'Donoghue triad most commonly used today.)[2][4][5]
-

Superior view of the structures in triad.
Injury
The unhappy triad occurs due to a lateral blow to the knee causing a rupture in the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament,and meniscus. Injury is most often sustained when a lateral (from the outside) force impacts the knee while the foot is fixed on the ground. The strong valgus or rotary force to the knee tears the ACL, MCL, and lateral meniscus all together. This type of injury occurs often in contact sports such as football, rugby, or motocross. During the injury, the leg is laterally rotated and over-abducted. In about 10% of cases the force is applied to the opposite side of the knee, and the lateral and posterolateral ligaments are torn.
Terminology
The term "unhappy triad" was coined by O'Donoghue in 1950.[2][6][7] However, since then, this term and the term "terrible triad" have also been used to describe several other combinations of joint injuries, including those of the elbow[8] and shoulder.[9]
The term "terrible triad" is also sometimes used in the popular press to describe conditions relating to pain, or even to refer to the MacDonald triad of sociopathic behavior.
Symptoms
- Pain in affected knee
- Stiffness and swelling in affected knee
- Catching or locking of the knee in affected knee
- Instability of the knee with twisting or side-to-side movements(The sensation of the knee "giving out").
- Inability to move the knee through its full range of motion
Epidemiology
A study containing 100 consecutive patients with a recent anterior cruciate ligament injury were examined with respect to type of sports activity that caused the injury. Of the 100 consecutive ACL injuries there were also, 53 medial collateral ligament injuries, 12 medial, 35 lateral and 11 bicompartmental meniscal lesions. 59/100 patients were injured during contact sports, 30/100 in downhill skiing and 11/100 in other recreational activities, traffic accidents or at work.[10]
An associated medial collateral ligament tear was more common in skiing (22/30) than during contact sports (23/59), whereas a bicompartmental meniscal lesion was found more frequently in contact sports (9/59) than in skiing (0/30). Weightbearing was reported by 56/59 of the patients with contact sports injuries whereas 8/30 of those with skiing injuries. Non-weightbearing in the injury situation led to the same rate of MCL tears (18/28) as weightbearing (35/72) but significantly more intact menisci (19/28 vs 23/72). Thus, contact sports injuries were more often sustained during weightbearing, with a resultant joint compression of both femuro-tibial compartments as shown by the higher incidence of bicompartmental meniscal lesions. The classic "unhappy triad" was a rare finding (8/100) and Fridén T, Erlandsson T, Zätterström R, Lindstrand A, and Moritz U. suggest that this entity should be replaced by the "unhappy compression injury".[10]
The anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four crucial ligaments in the knee. It originates from the lateral condyle of the femur and goes to the intercondyloid eminence of the tibia. Its function is to provide stability in the knee and minimize stress across the knee joint. It also restrains excessive forward movement in the leg and limits rotational movements in the knee.
Anterior cruciate ligament tear:
Injury

An anterior cruciate ligament injury results from excess tension the ligament. This can be done from a sudden stop or twisting motion of the knee. A few initial symptoms include swelling, knee instability, and pain. A popping sound or sensation may or may not be heard when the ACL first tears. A following symptom usually includes the feeling of the knee "giving out". Tearing of the ACL is the most significant injury because it leaves the knee unstable, which also causes the knee to lose its normal function.
Epidemiology
It is estimated that 100,000 new anterior cruciate ligament injuries occur in the U.S. each year.[11] Approximately half of the new ACL injuries involve injuries to the ligament, tendon, and or muscle of that affected knee.[12] Women are at greater risk for ACL injuries than men due to their greater Q angle. The Q angle is the angle formed by a line drawn from the anterior superior iliac spine to central patella and a second line drawn from central patella to tibial tubercle.
Meniscus

The medial meniscus is a C-wedge shaped piece of cartilage that acts as "shock absorbers" between the femur and the tibia. Each knee has two menisci, one at the outer edge and one at the inner edge of the knee. The menisci are tough and rubber-like to help cushion the joint and help keep it stable.
The lateral meniscus is also known as the external semilunar fibrocartilage. It is a fibrocartilage band on the lateral side of the knee joint and can easily be injured with torsional stress or direct force.
Each knee has a medial and lateral meniscus, which consist of connective tissue and collagen fibers. Meniscus is needed to distribute the body weight across the knee. Without the meniscus the body weight is distributed unevenly on the femur and tibia possibly leading to early arthritis to the knee joint. The meniscus is nourished by small blood vessels, but it has a large central section which is avascular and does not get direct blood supply. This poses a problem in a meniscus injury as blood flow is diminished and the avascular areas tend to not heal.
Injury
The tear of meniscus is among the most common knee injuries. It is usually caused by torsional stress; twisting or turning of the knee too quickly with the foot planted on the ground while the knee is flexed. The feeling of a "pop" in the knee is usually felt when the meniscus is torn. Athletes, particularly those who participate in contact sports, are at a greater risk for meniscal tears. Sports-related meniscal tears often occur with other knee injuries, such as an anterior cruciate ligament tear.
A torn meniscus is commonly referred to as a torn cartilage in the knee. Menisci tear in different ways and are noted by how they look, as well as where the tear occurs in the meniscus. Two types of tears include minor, which includes stiffness and swelling within two to three days but usually goes away in two to three weeks. Then there is severe, which without treatment, a piece of meniscus may come loose and drift into the joint space. Tears include longitudinal, parrot-beak, flap, bucket handle, and mixed/complex. Image of meniscal tear
Epidemiology
Injury to the medial meniscus is about five times greater than injury to the lateral meniscus due to its anatomical attachment to the MCL.[13] Lateral meniscal tears are more common in acute ACL injuries whereas medial mensical injuries are more common in chronic ACL deficient knees are more amenable to repair.[14]
Meta-analysis shows that in acute injuries of the ACL associated with a meniscus tear 44% were of the medial meniscus whereas 56% were of the lateral meniscus; in chronic ACL insufficiency 70% were medial whereas 30% were lateral.[15]
Medial Collateral Ligament
Injury
Because the medial collateral ligament resists widening of the inside of the knee joint, the ligament is usually injured when the outside of the knee joint is struck. This force causes the outside of the knee to buckle, and the inside to widen. When the MCL is stretched too far, it is susceptible to tearing and injury. This is the injury seen by the action of "clipping" in a football game.
An injury to the MCL may occur as an isolated injury, or it may be part of a complex injury to the knee. Other ligaments ACL, or meniscus, may be torn along with a MCL injury
Symptoms
The most common symptom following an MCL injury is pain directly over the ligament. Swelling over the torn ligament may appear, and bruising and generalized joint swelling are common 1 to 2 days after the injury. In more severe injuries, patients may complain that the knee feels unstable
Treatment
Treatment of an MCL tear depends on the severity of the injury. Treatment always begins with allowing the pain to subside, beginning work on mobility, followed by strengthening the knee to return to sports and activities. Bracing can often be useful for treatment of MCL injuries. Fortunately, most often surgery is not necessary for the treatment of an MCL tear.
Treatments For Unhappy Triad Injury
Treatment of the unhappy triad usually requires surgery. An ACL surgery is common and the meniscus can be treated during the surgery as well. The MCL is rehabilitated through time and immobilization. Physical therapy after the surgery and the use of a knee brace helps speed up the healing process. A typical surgery for a blown knee includes:
- Patellar tendon autograft (autograft comes from the patient)
- Hamstring tendon autograft
- Quadriceps tendon autograft
- Allograft (taken from a cadaver) patellar tendon, Achilles tendon, semitendinosus, gracilis, or posterior tibialis tendon
The goal of reconstruction surgery is to prevent instability and restore the function of the torn ligament, creating a stable knee. There are certain factors that the patient must consider when deciding for or against surgery.
See also
Additional images
-

Left knee-joint from behind, showing interior ligaments.
-
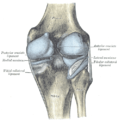
Capsule of right knee-joint (distended). Posterior aspect.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Shelbourne K, Nitz P (1991). "The O'Donoghue triad revisited. Combined knee injuries involving anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligament tears". Am J Sports Med 19 (5): 474–7. doi:10.1177/036354659101900509. PMID 1962712.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Barber, FA (1992). "What is the terrible triad?". Arthroscopy 8 (1): 19–22. doi:10.1016/0749-8063(92)90130-4. PMID 1550645.
- ↑ Winterstein, Andrew P. (2009). Athletic training student primer : a foundation for success (2nd ed.). Thorofare, NJ: SLACK. pp. 109–110. ISBN 978-1-55642-804-3.
- ↑ Balmer K, Gunst M, Rüedi T (January 1983). "[The "unhappy triad" (UT): slogan or reality in fresh knee injuries?]". Helv Chir Acta (in German) 49 (5): 675–7. PMID 6687587.
- ↑ Staron RB, Haramati N, Feldman F, et al. (November 1994). "O'Donoghue's triad: magnetic resonance imaging evidence". Skeletal Radiol. 23 (8): 633–6. doi:10.1007/BF02580384. PMID 7886473.
- ↑ O'Donoghue D (1950). "Surgical treatment of fresh injuries to the major ligaments of the knee". J Bone Joint Surg Am 32 (A:4): 721–38. PMID 14784482.
- ↑ O'Donoghue D (1964). "The unhappy triad: Etiology, diagnosis and treatment". Am J Orthop 6: 242–7 PASSIM. PMID 14237439.
- ↑ Pugh D, McKee M (2002). "The "terrible triad" of the elbow". Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg 6 (1): 21–9. doi:10.1097/00130911-200203000-00005. PMID 16520629.
- ↑ Simonich S, Wright T (2003). "Terrible triad of the shoulder". J Shoulder Elbow Surg 12 (6): 566–8. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(03)00216-7. PMID 14671520.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Fridén T, Erlandsson T, Zätterström R, Lindstrand A, Moritz U (1995). "Compression or distraction of the anterior cruciate injured knee. Variations in injury pattern in contact sports and downhill skiing". Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 3 (3): 144–7. PMID 8821269.
- ↑ Nedeff DD, Bach BR (2001). "Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using patellar tendon autografts: a comprehensive review of contemporary literature". Am J Knee Surg 14 (4): 243–58. PMID 11703038.
- ↑ Alford, MD, J. Winslow; Bernard R. Bach, Jr, MD (July 2001). "Managing ACL tears: evaluation and diagnosis". The Journal of Musculoskeletal Medicine: 381–390.
- ↑ Imaging of Orthopedic Sports Injuries (Medical Radiology / Diagnostic Imaging). Berlin: Springer. 2006. ISBN 3-540-26014-5.
- ↑ Johnson, Glen O.; Starkey, Chad (2005). Athletic training and sports medicine. Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 0-7637-0536-5.
- ↑ Bellabarba C, Bush-Joseph CA, Bach BR (January 1997). "Patterns of meniscal injury in the anterior cruciate-deficient knee: a review of the literature". Am J. Orthop. 26 (1): 18–23. PMID 9021030.
External links
- knee/clinicalcorr/clinicalcorr1 at the Dartmouth Medical School's Department of Anatomy
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
