Umbilical artery
| Artery: Umbilical artery | |
|---|---|
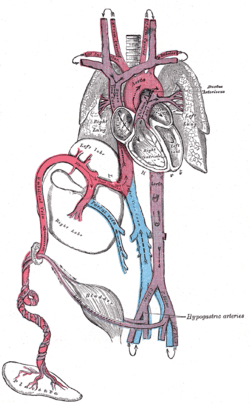 | |
| Fetal circulation; the umbilical vein is the large, red vessel at the far left. The umbilical arteries are purple and wrap around the umbilical vein. | |
 | |
| Scheme of placental circulation. | |
| Latin | Arteria umbilicalis |
| Gray's | p.540 |
| Source | internal iliac artery |
| Branches | superior vesical artery artery of the ductus deferens |
| Vein | umbilical vein |
| MeSH | Umbilical+Arteries |
The umbilical artery is a paired artery (with one for each half of the body) that is found in the abdominal and pelvic regions. In the fetus, it extends into the umbilical cord.
Umbilical arteries in the fetus
Umbilical arteries supply deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta in the umbilical cord. There are usually two umbilical arteries present together with one umbilical vein in the cord. The umbilical arteries are actually the latter of the internal iliac arteries (anterior division of) that supply the hind limbs with blood and nutrients in the fetus. The umbilical arteries surround the urinary bladder and then carry all the deoxygenated blood out of the fetus through the umbilical cord.
The umbilical arteries are the only arteries in the human body, aside from the pulmonary arteries, that carry deoxygenated blood.
The pressure inside the umbilical artery is approximately 50 mmHg.[1]
Inside the placenta, the umbilical arteries connect with each other at a distance of approximately 5 mm from the cord insertion in what is called the Hyrtl anastomosis.[2] Subsequently, they branch into chorionic arteries or intraplacental fetal arteries.[3]
Umbilical artery in the adult
The umbilical artery is a branch of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery and represents the patent (open) part of the embryonic umbilical artery. (The non-patent obliterated part of the artery is the medial umbilical ligament.) The umbilical artery is found in the pelvis, and gives rise to the superior vesical arteries. In males, it also gives rise to the artery to the ductus deferens.
Additional images
-

Model of human embryo 1.3 mm. long.
-
Transverse section of human embryo eight and a half to nine weeks old.
-
Tail end of human embryo twenty-five to twenty-nine days old.
-
Inguinal fossae
-
Umbilical artery.Deep dissection. Anterior view.
See also
References
- ↑ Fetal and maternal blood circulation systems From Online course in embryology for medicine students. Universities of Fribourg, Lausanne and Bern (Switzerland). Retrieved on 6 April 2009
- ↑ Gordon, Z.; Elad, D.; Almog, R.; Hazan, Y.; Jaffa, A. J.; Eytan, O. (2007). "Anthropometry of fetal vasculature in the chorionic plate". Journal of Anatomy 211 (6): 698–706. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00819.x. PMC 2375851. PMID 17973911.
- ↑ Hsieh, FJ; Kuo, PL; Ko, TM; Chang, FM; Chen, HY (1991). "Doppler velocimetry of intraplacental fetal arteries". Obstetrics and gynecology 77 (3): 478–82. PMID 1992421.
External links
- 1349189694 at GPnotebook
- 43:13-0203 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: Branches of Internal Iliac Artery"
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

