Umbellic acid
| Umbellic acid | |
|---|---|
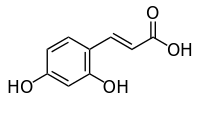 | |
| IUPAC name (E)-3-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid | |
| Other names 2,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 614-86-8 |
| PubChem | 446611 |
| ChemSpider | 393925 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molar mass | 180.16 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Umbellic acid (2,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid) is a hydroxycinnamic acid. It is an isomer of caffeic acid.
It is a precursor in the umbelliferone biosynthesis pathway. Umbelliferone is a phenylpropanoid and as such is synthesized from L-phenylalanine, which in turn is produced via the shikimate pathway. Phenylalanine is lysated into cinnamic acid, followed by hydroxylation by cinnamate 4-hydroxylase to yield 4-coumaric acid. The 4-coumaric acid is again hydroxylated by cinnamate/coumarate 2-hydroxylase to yield 2,4-dihydroxy-cinnamic acid followed by a bond rotation of the unsaturated bond adjacent to the carboxylic acid group. Finally an intramolecular attack from the hydroxyl group of C2' to the carboxylic acid group closes the ring and forms the lactone umbelliferone.
The enzyme 4-hydroxycinnamate decarboxylase, induced in bacteria species such as Klebsiella oxytoca, works also with p-coumaric acid analogs such as E-2,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid.[1]
References
External links
![]() The dictionary definition of umbellic acid at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of umbellic acid at Wiktionary
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||