UTC+03:00
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 | |
| Meridians | |
|---|---|
| Central | 45 degrees E |
| Western border (nautical) | 37.5 degrees E |
| Eastern border (nautical) | 52.5 degrees E |
| Other | |
| Date-time group (DTG) | C |
| External links | |
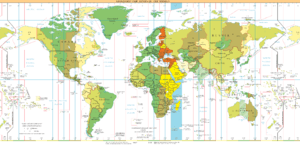
UTC+03:00 - 2011: Orange (DST Northern Hemisphere), Yellow (all year round), Light Blue - Sea areas

Time zones of Europe:
Light colours indicate countries that do not observe summer time: Algeria, Belarus, Iceland, Russia, Tunisia.
| light blue | Western European Time (UTC+0) |
| blue | Western European Time (UTC+0) Western European Summer Time (UTC+01:00) |
| pink | Central European Time (UTC+01:00) |
| brown | Central European Time (UTC+01:00) Central European Summer Time (UTC+02:00) |
| yellow | Eastern European Time (UTC+02:00) Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+03:00) |
| orange | Further-eastern European Time (UTC+03:00) |
| light green | Moscow Time (UTC+04:00) |

Time zones of Africa:
Striped colours indicate countries observing daylight saving time. Outside Africa the zones may have other names and summer time rules not indicated in this figure.
| UTC−01:00 | Cape Verde Time (The islands of Cape Verde are to the west of the African mainland.) | |
| UTC±00:00 | Western European Time · Greenwich Mean Time | |
| UTC+01:00 | Central European Time · West Africa Time · Western European Summer Time. | |
| UTC+02:00 | Central Africa Time · Eastern European Time · South African Standard Time · West Africa Summer Time | |
| UTC+03:00 | East Africa Time | |
| UTC+04:00 | Mauritius Time · Seychelles Time |

Time in Russia
| Time | Zone | |
|---|---|---|
| UTC+03:00 | MSK−1: Kaliningrad Time | |
| UTC+04:00 | MSK: Moscow Time | |
| UTC+06:00 | MSK+2: Yekaterinburg Time | |
| UTC+07:00 | MSK+3: Omsk Time | |
| UTC+08:00 | MSK+4: Krasnoyarsk Time | |
| UTC+09:00 | MSK+5: Irkutsk Time | |
| UTC+10:00 | MSK+6: Yakutsk Time | |
| UTC+11:00 | MSK+7: Vladivostok Time | |
| UTC+12:00 | MSK+8: Magadan Time |
UTC+03:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +03. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as 2014-02-13T04:35:32+03:00.
As standard time (all year round)
East Africa Time
- Comoros
- Djibouti
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Kenya
- Madagascar
- Mayotte (France) and Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean (Bassas da India, Europa Island, Juan de Nova Island)
- Somalia
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Tanzania
- Uganda
Eastern Europe Forward Time (EEFT), or Further-eastern European Time (FET)
Since September 2011 the following areas in Eastern Europe use UTC+3 all year round:
- Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, Kaliningrad Time
- Belarus, Minsk Time
Arabia Standard Time
Arabia Standard Time, or AST, is used by some countries in the Middle East. As this time zone is predominantly in the equatorial region, there is no significant change in day length throughout the year, so daylight saving time is not observed. Arabia Standard Time is used by the following countries:[1]
Notes:
- The westernmost point at which UTC+03 with no DST is applied is the Russian town of Baltiysk, in the Kaliningrad Oblast, at 19°55′E. Before 27 March 2011, it was the westernmost point of Sudan, in the West Darfur state, at the border with Chad; Geneina, the capital of West Darfur, located very close to that point, has a longitude of 22°27' E.
- The easternmost point at which UTC+03 with no DST is applied is actually the easternmost point of Saudi Arabia, in the Eastern Province, at the border with Oman, with a longitude of roughly 55°20' E.
As standard time (Northern Hemisphere winter only)
Formerly Moscow Time, before 27 March 2011; now UTC+4.[2]
As daylight saving time (Northern Hemisphere summer only)
Eastern European Summer Time - Territories observing European Union DST rules
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus (including Akrotiri and Dhekelia (UK) and Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus)
- Estonia
- Finland (including Åland)
- Greece
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Ukraine
- Moldova
- Romania
- Turkey
Middle East - observing various DST rules
See also
Notes
- The westernmost point at which UTC+03 with DST is applied is actually the westernmost point of contiguous Russia, near Lavry, Pskov Oblast (27°19' E). During the summer the time employed there (corresponding to 60°E) is 33°41' E of physical time, i.e. roughly 2 hours and 14 minutes ahead of physical time, making for the largest discrepancy between time used and physical time for UTC+3 with DST. This actually the largest discrepancy overall for UTC+03 even if UTC+03 with no DST is included.
- The easternmost point at which UTC+03 with DST is applied is Cape Zhelaniya, Severny Island, Novaya Zemlya, Russia (69°06' E). During the winter the time employed there (corresponding to 45°E) is 24°06' W of physical time, i.e. roughly 1 hour and 36 minutes behind physical time, making for the largest discrepancy between time used and physical time for UTC+3 with DST for that time of the year, but not overall (see note 1 above).
- On February 8, 2011, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev issued a decree cancelling DST in Russia. Under the decree, all clocks in Russia will advance one hour on March 27, 2011, but will not change back the following October, effectively making Kaliningrad Time UTC+03 permanently, and Moscow Time UTC+04 permanently.
- Ukraine had UTC+2 plus regularly EEST from 1992 till 2011 (in years 1981–89 Moscow Summer Time) until the Ukrainian parliament added one hour "on the territory of Ukraine from March 27, 2011" and canceled DST on September 20, 2011 de facto making EEST (UTC+3) the new standard time.[3] After strong criticism from the mass media, on 18 October 2011 the Ukrainian parliament cancelled its previous decision.[4]
References
- ↑ "AST – Arabia Standard Time". timeanddate.com. Retrieved 31 August 2011.
- ↑ "Russia Abolishes Winter Time". Timeanddate.com. 2011-02-08. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ↑ Ukraine cancels use of daylight saving time, Kyiv Post (September 20, 2011)
- ↑ "Ukraine to return to standard time on Oct. 30 (updated)". Kyiv Post. 18 October 2011. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.