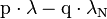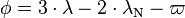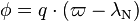Resonant trans-Neptunian object
|
|
‡ Trans-Neptunian dwarf planets are called "plutoids" |
In astronomy, a resonant trans-Neptunian object is a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) in mean motion orbital resonance with Neptune. The orbital periods of the resonant objects are in a simple integer relations with the period of Neptune e.g. 1:2, 2:3 etc. Resonant TNOs can be either part of the main Kuiper belt population, or the more distant scattered disc population.[1]
Distribution

The diagram illustrates the distribution of the known trans-Neptunian objects (up to 70 AU) in relation to the orbits of the planets together with centaurs for reference. Resonant objects are plotted in red. Orbital resonances with Neptune are marked with vertical bars; 1:1 marks the position of Neptune’s orbit (and its trojans), 2:3 marks the orbit of Pluto and plutinos, and 1:2, 2:5 etc. mark a number of smaller families.
The designation 2:3 or 3:2 refer both to the same resonance for TNOs. There’s no confusion possible as TNOs, by definition, have periods longer than Neptune. The usage depends on the author and the field of research. The statement "Pluto is in 2:3 resonance to Neptune" appears better to capture the meaning: Pluto completes 2 orbits for every 3 orbits of Neptune.
Origin
Detailed analytical and numerical studies[2][3] of Neptune’s resonances have shown that they are quite "narrow" (i.e. the objects must have a relatively precise range of energy). If the object semi-major axis is outside these narrow ranges, the orbit becomes chaotic, with widely changing orbital elements.
As TNOs were discovered, a substantial (more than 10%) proportion were found to be in 2:3 resonances, far from a random distribution. It is now believed that the objects have been collected from wider distances by sweeping resonances during the migration of Neptune.[4]
Well before the discovery of the first TNO, it was suggested that interaction between giant planets and a massive disk of small particles would, via momentum transfer, make Jupiter migrate inwards while Saturn, Uranus and especially Neptune would migrate outwards. During this relatively short period of time, Neptune’s resonances would be sweeping the space, trapping objects on initially-varying heliocentric orbits into resonance.[5]
Known populations
2:3 resonance ("plutinos", period ~250 years)

The 2:3 resonance at 39.4 AU is by far the dominant category among the resonant objects, with 92 confirmed and 104 possible member bodies.[6] The objects following orbits in this resonance are named plutinos after Pluto, the first such body discovered. Large, numbered plutinos include:[7]
- 90482 Orcus
- (84922) 2003 VS2
- 2003 AZ84
- 28978 Ixion
- 38628 Huya
3:5 resonance (period ~275 years)
A population of 10 objects at 42.3 AU as of October, 2008, including:[7]
- (126154) 2001 YH140
- (15809) 1994 JS
- (143751) 2003 US292
4:7 resonance (period ~290 years)
Another important population of objects (20 identified as of October 2008) is orbiting the Sun at 43.7 AU (in the midst of the classical objects). The objects are rather small (with a single exception, H>6) and most of them follow orbits close to the ecliptic. Objects with well established orbits include:[7]
- 1999 CD158, the largest
- (119956) 2002 PA149
- (119070) 2001 KP77
- (118378) 1999 HT11
- (118698) 2000 OY51
1:2 resonance ("twotinos", period ~330 years)
This resonance at 47.8 AU is often considered as the outer "edge" of the Kuiper belt and the objects in this resonance are sometimes referred to as twotinos. Twotinos have inclinations less than 15 degrees and generally moderate eccentricities (0.1 < e < 0.3).[8] An unknown number of the 2:1 resonants likely did not originate in a planetesimal disk that was swept by the resonance during Neptune's migration.[9]
There are far fewer objects in this resonance (a total of 14 as of October, 2008) than plutinos. Long-term orbital integration shows that the 1:2 resonance is less stable than 2:3 resonance; only 15% of the objects in 1:2 resonance were found to survive 4 Gyr as compared with 28% of the plutinos.[8] Consequently it might be that twotinos were originally as numerous as plutinos, but their population has dropped significantly below that of plutinos since.[8]
Objects with well established orbits include (in order of the absolute magnitude):[7]
- (119979) 2002 WC19
- (26308) 1998 SM165
- (137295) 1999 RB216
- (20161) 1996 TR66
- (130391) 2000 JG81

2:5 resonance (period ~410 years)
Objects with well established orbits at 55.4 AU include:[7]
- (84522) 2002 TC302, a large dwarf-planet candidate
- (143707) 2003 UY117
- (119068) 2001 KC77
- (135571) 2002 GG32
- (69988) 1998 WA31
In total, the orbits of 11 objects are classified as 2:5 as of October, 2008.
Other resonances
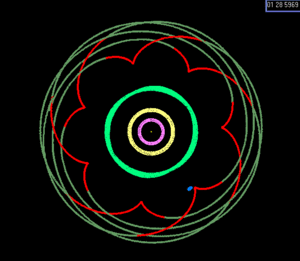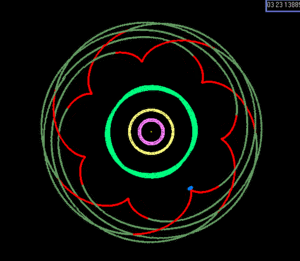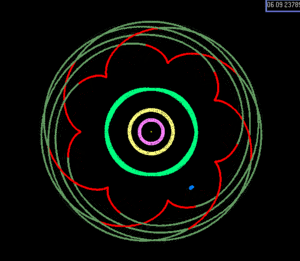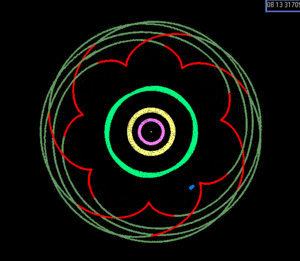
So called higher-order resonances are known for a limited number of objects, including the following numbered objects[7]
- 4:5 (35 AU, ~205 years) (131697) 2001 XH255
- 3:4 (36.5 AU, ~220 years) (143685) 2003 SS317, (15836) 1995 DA2
- 5:9 (44.5 AU, ~295 years) 2002 GD32[10]
- 4:9 (52 AU, ~370 years) (42301) 2001 UR163, (182397) 2001 QW297[11]
- 3:7 (53 AU, ~385 years) (131696) 2001 XT254, (95625) 2002 GX32, (183964) 2004 DJ71, (181867) 1999 CV118
- 5:12 (55 AU, ~395 years) (79978) 1999 CC158, (119878) 2001 CY224[12] (84% probability according to Emel’yanenko)
- 3:8 (57 AU, ~440 years) (82075) 2000 YW134[13] (84% probability according to Emel’yanenko)
- 3:10 (67 AU, ~549 years) (225088) 2007 OR10
- 2:7 (70 AU, ~580 years) 2006 HX122[14] (The preliminary orbit suggests a weak 2:7 resonance. Further observations will be required.)
A few objects are known on simple, distant resonances[7]
- 1:3 (62.5 AU, ~495 years) (136120) 2003 LG7
- 1:4 (76 AU, ~660 years) 2003 LA7[15]
- 1:5 (88 AU, ~820 years) 2003 YQ179 (likely coincidental)[16]
Some notable unproven (they could be coincidental) dwarf planet resonances include:
- 7:12 (43 AU, ~283 years) Haumea[17] (nominal orbit very likely in resonance)
- 6:11 (45 AU, ~302 years) Makemake[18] ((182294) 2001 KU76 appears to be in the 6:11 resonance)
- 5:17 (67 AU, ~560 years) Eris[18] (2007 OR10 has a similar orbit)
1:1 resonance (Neptune trojans, period ~165 years)
A few objects have been discovered following orbits with semi-major axes similar to that of Neptune, near the Sun–Neptune Lagrangian points. These Neptune trojans, termed by analogy to the (Jupiter) Trojan asteroids, are in 1:1 resonance with Neptune. Nine are known as of October 2012:
Only the last three objects are near Neptune's L5 Lagrangian point; the others are located in Neptune's L4 region.[19]
Coincidental versus true resonances
One of the concerns is that weak resonances may exist and would be difficult to prove due to the current lack of accuracy in the orbits of these distant objects. Many objects have orbital periods of more than 300 years and most have only been observed over a short observation arc of a couple years. Due to their great distance and slow movement against background stars, it may be decades before many of these distant orbits are determined well enough to confidently confirm whether a resonance is true or merely coincidental. A true resonance will smoothly oscillate while a coincidental near resonance will circulate. (See Toward a formal definition)
Simulations by Emel’yanenko and Kiseleva in 2007 show that (131696) 2001 XT254 is librating in a 7:3 resonance with Neptune.[20] This libration can be stable for less than 100 million to billions of years.[20]

Emel’yanenko and Kiseleva also show that (48639) 1995 TL8 appears to have less than a 1% probability of being in a 7:3 resonance with Neptune, but it does execute circulations near this resonance.[20]

Toward a formal definition
The classes of TNO have no universally agreed precise definitions, the boundaries are often unclear and the notion of resonance is not defined precisely. The Deep Ecliptic Survey introduced formally defined dynamical classes based on long-term forward integration of orbits under the combined perturbations from all four giant planets. (see also formal definition of classical KBO)
In general, the mean motion resonance may involve not only orbital periods of the form
where p and q are small integers, λ and λN are respectively the mean longitudes of the object and Neptune, but can also involve the longitude of the perihelion and the longitudes of the nodes (see orbital resonance, for elementary examples)
An object is a Resonant if for some small integers p,q,n,m,r,s, the argument (angle) defined below is librating (i.e. is bounded)[21]
where the 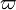 are the longitudes of perihelia and the
are the longitudes of perihelia and the  are the longitudes of the ascending nodes, for Neptune (with subscripts "N") and the resonant object (no subscripts).
are the longitudes of the ascending nodes, for Neptune (with subscripts "N") and the resonant object (no subscripts).
The term libration denotes here periodic oscillation of the angle around some value and is opposed to circulation where the angle can take all values from 0 to 360°. For example, in the case of Pluto, the resonant angle  librates around 180° with an amplitude of around 82° degrees, i.e. the angle changes periodically from 180°-82° to 180°+82°.
librates around 180° with an amplitude of around 82° degrees, i.e. the angle changes periodically from 180°-82° to 180°+82°.
All new plutinos discovered during the Deep Ecliptic Survey proved to be of the type
similar to Pluto's mean motion resonance.
More generally, this 2:3 resonance is an example of the resonances p:(p+1) (example 1:2, 2:3, 3:4 etc.) that have proved to lead to stable orbits.[4] Their resonant angle is
In this case, the importance of the resonant angle 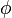 can be understood by noting that when the object is at perihelion, i.e.
can be understood by noting that when the object is at perihelion, i.e. 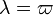 , then
, then
i.e. 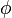 gives a measure of the distance of the object's perihelion from Neptune.[4]
The object is protected from the perturbation by keeping its perihelion far from Neptune provided
gives a measure of the distance of the object's perihelion from Neptune.[4]
The object is protected from the perturbation by keeping its perihelion far from Neptune provided 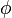 librates around an angle far from 0°.
librates around an angle far from 0°.
Classification methods
As the orbital elements are known with a limited precision, the uncertainties may lead to false positives (i.e. classification as resonant of an orbit which is not).
A recent approach[22] considers not only the current best-fit orbit but also two additional orbits corresponding to the uncertainties of the observational data. In simple terms, the algorithm determines whether the object would be still classified as resonant if its actual orbit differed from the best fit orbit, as the result of the errors in the observations.
The three orbits are numerically integrated over a period of 10 million years. If all three orbits remain resonant (i.e. the argument of the resonance is librating, see formal definion), the classification as a resonant object is considered secure.[22]
If only two out of the three orbits are librating the object is classified as probably in resonance. Finally, if only one orbit passes the test, the vicinity of the resonance is noted to encourage further observations to improve the data.[22]
The two extreme values of the semi-major axis used in the algorithm are determined to correspond to uncertainties of the data of at most 3 standard deviations. Such range of semi-axis values should, with a number of assumptions, reduce the probability that the actual orbit is beyond this range to less than 0.3%.
The method is applicable to objects with observations spanning at least 3 oppositions.[22]
References
- ↑ Hahn J. Malhotra R.Neptune's migration into a stirred-up Kuiper Belt The Astronomical Journal, 130, pp.2392-2414, Nov.2005.Full text on arXiv.
- ↑ Malhotra, Renu The Phase Space Structure Near Neptune Resonances in the Kuiper Belt. Astronomical Journal v.111, p.504 preprint
- ↑ E. I. Chiang and A. B. Jordan, On the Plutinos and Twotinos of the Kuiper Belt, The Astronomical Journal, 124 (2002), pp.3430–3444. (html)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Renu Malhotra, The Origin of Pluto's Orbit: Implications for the Solar System Beyond Neptune, The Astronomical Journal, 110 (1995), p. 420 Preprint.
- ↑ Malhotra, R.; Duncan, M. J.; Levison, H. F. Dynamics of the Kuiper Belt. Protostars and Planets IV, University of Arizona Press, p. 1231 preprint
- ↑ Trans-Neptunian objects
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 List of the classified orbits from MPC October, 2008
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 M. Tiscareno, R. Malhotra (April 2008). "Chaotic Diffusion of Resonant Kuiper Belt Objects". The Astronomical Journal 194 (3): 827–837. arXiv:0807.2835. Bibcode:2009AJ....138..827T. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/138/3/827.
- ↑ Lykawka, Patryk Sofia & Mukai, Tadashi (July 2007). "Dynamical classification of trans-neptunian objects: Probing their origin, evolution, and interrelation". Icarus 189 (1): 213–232. Bibcode:2007Icar..189..213L. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2007.01.001.
- ↑ Marc W. Buie (2005-04-11 using 20 observations). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 02GD32". SwRI (Space Science Department). Retrieved 2009-02-05.
- ↑ Marc W. Buie (2007-11-09 using 23 observations). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 182397". SwRI (Space Science Department). Retrieved 2009-01-29.
- ↑ Marc W. Buie (2005-12-06 using 41 observations). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 119878". SwRI (Space Science Department). Retrieved 2009-01-29.
- ↑ Marc W. Buie (2004-04-16 using 62 of 63 observations). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 82075". SwRI (Space Science Department). Retrieved 2009-01-29.
- ↑ "MPEC 2008-K28 : 2006 HX122". Minor Planet Center. 2008-05-23. Retrieved 2009-01-30.
- ↑ Marc W. Buie (2007-04-21 using 13 of 14 observations). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 03LA7". SwRI (Space Science Department). Retrieved 2009-01-29.
- ↑ Marc W. Buie (2008-03-03 using 23 of 24 observations). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 03YQ179". SwRI (Space Science Department). Retrieved 2009-01-29.
- ↑ D. Ragozzine; M. E. Brown (2007-09-04). "Candidate Members and Age Estimate of the Family of Kuiper Belt Object 2003 EL61". The Astronomical Journal 134 (6): 2160–2167. arXiv:0709.0328. Bibcode:2007AJ....134.2160R. doi:10.1086/522334.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Tony Dunn. "Possible resonances of Eris (2003 UB313) and Makemake (2005 FY9)". Gravity Simulator. Retrieved 2009-01-29.
- ↑ "List Of Neptune Trojans". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 2013-01-08.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 Emel’yanenko, V. V; Kiseleva, E. L. (2008). "Resonant motion of trans-Neptunian objects in high-eccentricity orbits". Astronomy Letters 34 (4): 271–279. Bibcode:2008AstL...34..271E. doi:10.1134/S1063773708040075.
- ↑ J. L. Elliot, S. D. Kern, K. B. Clancy, A. A. S. Gulbis, R. L. Millis, M. W. Buie, L. H. Wasserman, E. I. Chiang, A. B. Jordan, D. E. Trilling, and K. J. Meech The Deep Ecliptic Survey: A Search for Kuiper Belt Objects and Centaurs. II. Dynamical Classification, the Kuiper Belt Plane, and the Core Population. The Astronomical Journal, 129 (2006), pp. preprint
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 B. Gladman, B. Marsden, C. VanLaerhoven (2008). "Nomenclature in the Outer Solar System". In The Solar System Beyond Neptune, ISBN 9780816527557.
Further reading
- John K. Davies and Luis H. Barrera, ed. (2004-08-03). The First Decadal Review of the Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt. Springer. ISBN 1-4020-1781-2.
- E. I. Chiang, J. R. Lovering, R. L. Millis, M. W. Buie, L. H. Wasserman, and K. J. Meech (June 2003). "Resonant and Secular Families of the Kuiper Belt". Earth, Moon, and Planets (Springer Netherlands) 92 (1–4): 49–62. Bibcode:2003EM&P...92...49C. doi:10.1023/B:MOON.0000031924.20073.d0.
- E. I. Chiang, A. B. Jordan, R. L. Millis, M. W. Buie, L. H. Wasserman, J. L. Elliot, S. D. Kern, D. E. Trilling, K. J. Meech, and R. M. Wagner (2003-01-21). "Resonance occupation in the Kuiper Belt: case examples of the 5:2 and trojan resonances". The Astronomical Journal (The American Astronomical Society) 126 (1): 430–443. arXiv:astro-ph/0301458. Bibcode:2003AJ....126..430C. doi:10.1086/375207.
- Renu Malhotra. The Kuiper Belt as a Debris Disk. (as HTML)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||