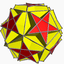
Truncated great icosahedron
| Truncated great icosahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Uniform star polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 32, E = 90 V = 60 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 12{5/2}+20{6} |
| Wythoff symbol(s) | 2 5/2 | 3 2 5/3 | 3 |
| Symmetry group | Ih, [5,3], *532 |
| Index references | U55, C71, W95 |
| Bowers acronym | Tiggy |
 6.6.5/2 (Vertex figure) |
 Great stellapentakis dodecahedron (dual polyhedron) |
In geometry, the truncated great icosahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U55. It is given a Schläfli symbol t0,1{3,5/2} as a truncated great icosahedron.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a truncated great icosahedron centered at the origin are all the even permutations of
- (±1, 0, ±3/τ)
- (±2, ±1/τ, ±1/τ3)
- (±(1+1/τ2), ±1, ±2/τ)
where τ = (1+√5)/2 is the golden ratio (sometimes written φ). Using 1/τ2 = 1 − 1/τ one verifies that all vertices are on a sphere, centered at the origin, with the radius squared equal to 10−9/τ. The edges have length 2.
Related polyhedra
This polyhedron is the truncation of the great icosahedron:
The truncated great stellated dodecahedron is a degenerate polyhedron, with 20 triangular faces from the truncated vertices, and 12 (hidden) pentagonal faces as truncations of the original pentagram faces, the latter forming a great dodecahedron inscribed within and sharing the edges of the icosahedron.
| Name | Great stellated dodecahedron |
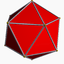
Truncated great stellated dodecahedron | Great icosidodecahedron |
Truncated great icosahedron |
Great icosahedron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram |
|||||
| Picture |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
See also
External links
| |||||||||||||||||