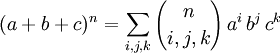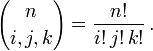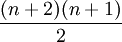Trinomial expansion
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematics, a trinomial expansion is the expansion of a power of a sum of three terms into monomials. The expansion is given by
where n is a nonnegative integer and the sum is taken over all combinations of nonnegative indices i, j, and k such that i + j + k = n. The trinomial coefficients are given by
This formula is a special case of the multinomial formula for m = 3. The coefficients can be defined with a generalization of Pascal's triangle to three dimensions, called Pascal's pyramid or Pascal's tetrahedron.
The number of terms of an expanded trinomial is
where n is the exponent to which the trinomial is raised.
See also
- Binomial expansion
- Pascal's pyramid
- Multinomial coefficient
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.