Trinomial
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about mathematics. For the use in taxonomy, see Trinomial name. For the use identifying archaeological sites in the United States, see Smithsonian trinomial.
In elementary algebra, a trinomial is a polynomial consisting of three terms or monomials.
Trinomial expressions
-
 with
with  variables
variables -
 with
with 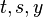 variables
variables -
 with
with 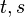 variables
variables -
 with
with 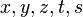 variables,
variables,  nonnegative integers and
nonnegative integers and  any constants.
any constants. -
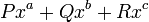 where
where  is variable and constants
is variable and constants  are nonnegative integers and
are nonnegative integers and 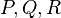 any constants.
any constants.
Trinomial equation
A trinomial equation is a polynomial equation involving three terms. An example is the equation  studied by Johann Heinrich Lambert in the 18th century.[1]
studied by Johann Heinrich Lambert in the 18th century.[1]
See also
- Trinomial expansion
- Monomial
- Binomial
- Multinomial
- Simple expression
- Compound expression
References
- ↑ Corless, R. M.; Gonnet, G. H.; Hare, D. E. G.; Jerey, D. J.; Knuth, D. E. (1996). "On the Lambert W Function". Advances in Computational Mathematics 5 (1): 329–359. doi:10.1007/BF02124750.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.