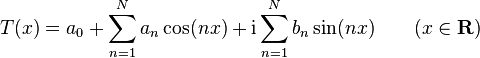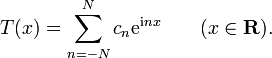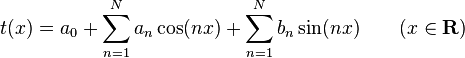Trigonometric polynomial
In the mathematical subfields of numerical analysis and mathematical analysis, a trigonometric polynomial is a finite linear combination of functions sin(nx) and cos(nx) with n taking on the values of one or more natural numbers. The coefficients may be taken as real numbers, for real-valued functions. For complex coefficients, there is no difference between such a function and a finite Fourier series.
Trigonometric polynomials are widely used, for example in trigonometric interpolation applied to the interpolation of periodic functions. They are used also in the discrete Fourier transform.
The term trigonometric polynomial for the real-valued case can be seen as using the analogy: the functions sin(nx) and cos(nx) are similar to the monomial basis for polynomials. In the complex case the trigonometric polynomials are spanned by the positive and negative powers of eix.
Formal definition
Any function T of the form
with an, bn in C for 0 ≤ n ≤ N, is called a complex trigonometric polynomial of degree N (Rudin 1987, p. 88). Using Euler's formula the polynomial can be rewritten as
Analogously let an, bn be in R, 0 ≤ n ≤ N and aN ≠ 0 or bN ≠ 0 then
is called real trigonometric polynomial of degree N (Powell 1981, p. 150).
Notes
A trigonometric polynomial can be considered a periodic function on the real line, with period some multiple of 2π, or as a function on the unit circle.
A basic result is that the trigonometric polynomials are dense in the space of continuous functions on the unit circle, with the uniform norm (Rudin 1987, Thm 4.25); this is a special case of the Stone–Weierstrass theorem. More concretely, for every continuous function ƒ and every ε > 0, there exists a trigonometric polynomial T such that |ƒ(z) − T(z)| < ε for all z. Fejér's theorem states that the arithmetic means of the partial sums of the Fourier series of ƒ converge uniformly to ƒ, thus giving an explicit way to find an approximating trigonometric polynomial T.
A trigonometric polynomial of degree N has a maximum of 2N roots in any open interval [a, a + 2π) with a in R, unless it is the zero function (Powell 1981, p. 150).
References
- Powell, Michael J. D. (1981), Approximation Theory and Methods, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-29514-7
- Rudin, Walter (1987), Real and complex analysis (3rd ed.), New York: McGraw-Hill, ISBN 978-0-07-054234-1, MR 924157.