Tricuspid atresia
| Tricuspid atresia | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
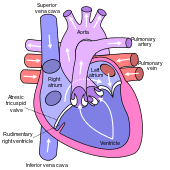 Anterior (frontal) view of the opened heart. White arrows indicate normal blood flow. (Tricuspid valve labeled at bottom left.) | |
| ICD-10 | Q22.4 |
| ICD-9 | 746.1 |
| OMIM | 605067 |
| MedlinePlus | 001110 |
| eMedicine | med/2313 |
| MeSH | D018785 |
Tricuspid atresia is a form of congenital heart disease whereby there is a complete absence of the tricuspid valve. Therefore, there is an absence of right atrioventricular connection. This leads to a hypoplastic (undersized) or absent right ventricle. This defect is contracted during prenatal development, when the heart does not finish developing. It causes the heart to be unable to properly oxygenate the rest of the blood in the body. Because of this, the body does not have enough oxygen to live, and steps must be taken to keep the child alive. Because of the lack of an A-V connection, an atrial septal defect (ASD) must be present to maintain blood flow. Also, since there is a lack of a right ventricle there must be a way to pump blood into the pulmonary arteries, and this is accomplished by a ventricular septal defect (VSD).
Blood is mixed in the left atrium. Because the only way the pulmonary circulation receives blood is through the VSD, a patent ductus arteriosus usually also persists to increase pulmonary flow.
Clinical manifestations
- progressive cyanosis
- poor feeding
- tachypnea over the first 2 weeks of life
- holosystolic murmur due to the VSD
- left axis deviation on electrocardiography and left ventricular hypertrophy (since it must pump blood to both the pulmonary and systemic systems)
- normal heart size
Treatment
- PGE1 to maintain patent ductus arteriosus
- modified Blalock-Taussig shunt to maintain pulmonary blood flow by placing a Gore-Tex conduit between the subclavian artery and the pulmonary artery.
- cavopulmonary anastomosis (hemi-Fontan or bidirectional Glenn) to provide stable pulmonary flow
- Fontan procedure to redirect inferior vena cava and hepatic vein flow into the pulmonary circulation
External links
- Tricuspid Atresia information from Seattle Children's Hospital Heart Center
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||