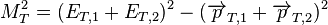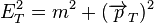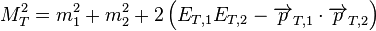Transverse mass
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The transverse mass is a useful quantity to define for use in particle physics as it is invariant under Lorentz boost along the z direction. In natural units it is:
- where the z-direction is along the beam pipe and so
 and
and 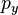 are the momentum perpendicular to the beam pipe and
are the momentum perpendicular to the beam pipe and is the mass.
is the mass.
Hadron collider physicists use another definition of transverse mass, in the case of a decay into two particles:
- where
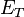 is the transverse energy of each daughter, a positive quantity defined using its true invariant mass
is the transverse energy of each daughter, a positive quantity defined using its true invariant mass  as:
as:
So equivalently,
For massless daughters, where 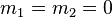 , the transverse energy simplifies to
, the transverse energy simplifies to  , and the transverse mass becomes
, and the transverse mass becomes
- where
 is the angle between the daughters in the transverse plane:
is the angle between the daughters in the transverse plane:
A distribution of 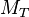 has an end-point at the true mother mass:
has an end-point at the true mother mass: 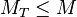 . This has been used to determine the
. This has been used to determine the 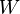 mass at the Tevatron.
mass at the Tevatron.
References
- J.D. Jackson (2008). "Kinematics". Particle Data Group. - See sections 38.5.2 (
 ) and 38.6.1 (
) and 38.6.1 (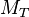 ) for definitions of transverse mass.
) for definitions of transverse mass. - J. Beringer et al. (2012). "Review of Particle Physics". Particle Data Group. - See sections 43.5.2 (
 ) and 43.6.1 (
) and 43.6.1 (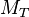 ) for definitions of transverse mass.
) for definitions of transverse mass.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.