Transition rate matrix
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In probability theory, a transition rate matrix (also known as an intensity matrix[1][2] or infinitesimal generator matrix[3]) is an array of numbers describing the rate a continuous time Markov chain moves between states.
In a transition rate matrix Q (sometimes written A[4]) element qij (for i ≠ j) denotes the rate departing from i and arriving in state j. Diagonal elements qii are defined such that
and therefore the rows of the matrix sum to zero.
Definition
A Q matrix (qij) satisfies the following conditions[5]
- 0 ≤ -qii ≤ ∞
- 0 ≤ qij for all i ≠ j
-
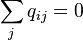 for all i.
for all i.
Example
An M/M/1 queue, a model which counts the number of jobs in a queueing system with arrivals at rate λ and services at rate μ, has transition rate matrix
References
- ↑ Syski, R. (1992). Passage Times for Markov Chains. IOS Press. doi:10.3233.2F978-1-60750-950-9-i. ISBN 90-5199-060-X.
- ↑ Asmussen, S. R. (2003). "Markov Jump Processes". Applied Probability and Queues. Stochastic Modelling and Applied Probability 51. pp. 39–59. doi:10.1007/0-387-21525-5_2. ISBN 978-0-387-00211-8.
- ↑ Trivedi, K. S.; Kulkarni, V. G. (1993). "FSPNs: Fluid stochastic Petri nets". Application and Theory of Petri Nets 1993. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 691. p. 24. doi:10.1007/3-540-56863-8_38. ISBN 978-3-540-56863-6.
- ↑ Rubino, Gerardo; Sericola, Bruno (1989). "Sojourn Times in Finite Markov Processes". Journal of Applied Probability (Applied Probability Trust) 26 (4): 744–756. JSTOR 3214379.
- ↑ Norris, J. R. (1997). Markov Chains. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511810633. ISBN 9780511810633.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.

