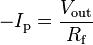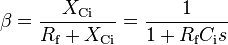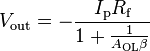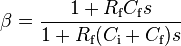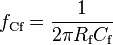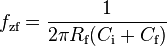Transimpedance amplifier

In electronics, a transimpedance amplifier, (TIA) is a current to voltage converter, most often implemented using an operational amplifier. The TIA can be used to amplify the current output of Geiger–Müller tubes, photo multiplier tubes, accelerometers, photo detectors and other types of sensors. Current to voltage converters are used with sensors that have a current response that is more linear than the voltage response. This is the case with photodiodes where it is not uncommon for the current response to have better than 1% linearity over a wide range of light input. The transimpedance amplifier presents a low impedance to the photodiode and isolates it from the output voltage of the operational amplifier. In its simplest form a transimpedance amplifier has just a large valued feedback resistor, Rf. The gain of the amplifer is set by this resistor and because the amplifer is in an inverting configuration, has a value of -Rf Ohms. There are several different configurations of transimpedance amplifiers, each suited to a particular application. The one factor they all have in common is the requirement to convert the low-level current of a sensor to a voltage. The gain, bandwidth, as well as current and voltage offsets change with different types of sensors, requiring different configurations of transimpedance amplifiers.[1]
DC Operation
In the circuit shown in Fig. 1 the photodiode is connected between ground and the inverting input of the opamp. The other input of the opamp is also connected to ground. This provides a low impedance load for the photodiode, which keeps the photodiode voltage low. The photodiode is operating in photovoltaic mode with no external bias. The high gain of the opamp keeps the photodiode current equal to the feedback current through Rf. The input offset voltage due to the photodiode is very low in this self-biased photovoltaic mode. This permits a large gain without any large output offset voltage. This configuration is used with photodiodes that are illuminated with low light levels and require a lot of gain.
and
The above equation is the DC and low frequency gain of a transimpedance amplifier. If the gain is large any input offset voltage at the non-inverting input of the opamp will result in an output DC offset. An input bias current on the inverting terminal of the opamp will similarly result in an output offset. To minimize these effects transimpedance amplifiers are usually designed with FET input opamps that have very low input offset voltages.[2]
Fig. 2 shows a TIA with the photodiode driven by a laser diode and operating in the photoconductive mode. A positive voltage at the cathode of the photodiode applies a reverse bias. This reverse bias increases the width of the depletion region and lowers the junction capacitance, improving the high frequency performance. The photoconductive configuration of a transimpedance photodiode amplifier is used where fast switching speed is required but high gain is not. The feedback capacitor, Cf is usually required to improve stability.
Bandwidth and Stability

The frequency response of a transimpedance amplifier is inversely proportional to the gain set by the feedback resistor. The product of the gain, Vin/Vo, is very close to being a constant for any given opamp. The sensors that transimpedance amplifiers are used with usually have more capacitance than an opamp can handle. Fig. 3 models the sensor as a current source and a capacitor, Ci.[3] This capacitance across the input terminals of the opamp, which includes the internal capacitance of the opamp, introduces a low-pass filter in the feedback path. The low pass response of this filter can be characterized as the feedback factor β, which attenuates the feedback signal. This places a greater demand on the amplifier gain.
where
-
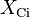 is the reactance of the capacitance Ci.
is the reactance of the capacitance Ci.
When the effect of this low-pass filter response is considered, the circuit's response equation becomes the following:
where
-
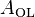 is the open loop gain of the opamp.
is the open loop gain of the opamp.

At low frequencies the feedback factor β has little effect on the amplifier response. The amplifier response will be close to the ideal,
as long as the loop gain,
is much greater than unity. The bode plot of a transimpedance amplifier with no compensation is shown in Fig. 4. The vertical axis represents logrithmic gain and the horizontal axis the log of frequency. The flat curve with the peak, labeled I-TO-V GAIN, is the frequency response of the transimpedance amplifier. The peaking of the gain curve is typical of uncompensated or poorly compensated transimpedance amplifiers. The curve labeled AOL is the open-loop response of the amplifier. The feedback factor, plotted as a reciprocal, is labeled 1/β. In Fig. 4 the 1/β curve and AOL form an equilateral triangle with the frequency axis. The two sides have equal but opposite slope since one is the result of a first order Pole (complex analysis) and the other a first order Zero (complex analysis). Each slope has a magnitude of 20 dB, corresponding to a phase shift of 90°. When the amplifier's 180° of phase inversion is added to this the result is a full 360° at the fi intercept, indicated by the dashed vertical line. At that intercept 1/β = AOL, for a loop gain of AOLβ = 1. Oscillation will occur at the fi frequency because of the 360° phase shift, or positive feedback, and the unity gain.[4] To mitigate these effects designers of transimpedance amplifiers add a small value compensating capacitor. Fig. 3 shows a capacitor, Cf in parallel with the feedback resistor. When this feedback capacitor is considered, the compensated feedback factor becomes:
The feedback capacitor produces a zero, or deflection in the response curve, at the frequency
This counteracts the pole produced by Ci at the frequency

Fig. 5 shows the bode plot of a transimpedance amplifier that has a compensation capacitor in the feedback path, as shown in Fig. 3. The compensated feedback factor, plotted as a reciprocal, 1/β, starts to roll off before fi, reducing the slope at the intercept. The loop gain is still unity but the total phase shift is not a full 360°. One of the requirements for oscillation is eliminated with the addition of the compensation capacitor and so the circuit has stability. This also reduces the gain peaking, producing a flater overall response. There are several methods used to calculate the compensation capacitor's value. A compensation capacitor that has too large a value will reduce the bandwidth of the amplifier. If the capacitor is too small oscillation may occur. [5] One difficulty with this method of phase compensation is the resulting small value of the capacitor and the iterative method often required to optimize the value. There is no cut and dry formula for calculating the capacitor value that works for all cases. A compensation method that uses a larger value capacitor that is not as susceptible to Parasitic capacitance effects can also be used.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ The Art of Electronics, Horowitz and Hill
- ↑ Design of a Modified Cherry-Hooper Transimpedance Amplifier with DC Offset Cancellation, Kyle LaFevre
- ↑ Photodiode Amplifiers p 39, Jerald Graeme
- ↑ Photodiode Amplifiers p 41, Jerald Graeme
- ↑ St. Pease on Transimpedance amplifiers
- ↑ Photodiode Amplifiers p 49, Jerald Graeme
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Current-to-voltage converter diagrams. |
- Low Current Measurements
- Using a low noise JFET in a Current to Voltage convertor circuit (TIA)
- Bootstrapping a large Photodiode in an I-to-V circuit (TIA)