Trading Path
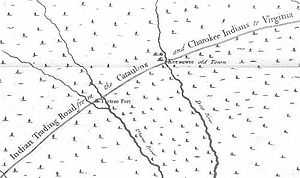
The Trading Path (a.k.a. Occaneechi Path, The Path to the Catawba, the Catawba Road, Indian Trading Path, Warriors' Path, etc.) is not simply one wide path, as many named historic roads were or are. It was a corridor of roads and trails between the Chesapeake Bay region (mainly the Petersburg, Virginia area) and the Cherokee, Catawba, and other Native-American groups in the Piedmont region of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. Indians had used and maintained much of the path for their expansive trading network centuries prior to its use by Europeans and/or European-Americans. Indian and later European/European-American settlements occupied key points along the path.
Both Natives and Newcomers mainly used the Trading Path for commercial cargo carriage. In early colonial times, Virginian traders used the path to travel to Native American towns in the Waxhaws. They led long pack caravans of horses carrying "loads of guns, gunpowder, knives, jewelry, blankets, and hatchets, among other goods", and travel southwest to Indian villages along the journey to the Waxhaws region, in the vicinity of present-day Mecklenburg County.[1] They exchanged European goods for furs and deerskins.
Because the path was well laid out through the complex geography of the piedmont area, connecting fords of many streams, it was roughly followed by the 19th-century railroad. Later, engineers who designed Interstate 85 followed much of this route again from Petersburg, VA, to roughly the Georgia state border. Many of the earliest towns along its route remain to this day. Many remnants of the Trading Path are still visible.
The Trading Path underlies the Piedmont Urban Crescent, which since the late 19th century has had steady growth. It is a spine of polycentric urban development in North Carolina. Cities of the Crescent are the centers of government, finance, education and research, and business in the state.
References
- ↑ "Trading Path, Marker L-35", North Carolina Historical Markers Highway Program, Department of Cultural Resources, accessed 3 Apr 2010