Total pressure
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In physics, the term total pressure may indicate two different quantities, both having the dimensions of a pressure:
- In fluid dynamics, total pressure (
 ) refers to the sum of static pressure p, dynamic pressure q, and gravitational head, as expressed by Bernoulli's principle:
) refers to the sum of static pressure p, dynamic pressure q, and gravitational head, as expressed by Bernoulli's principle:
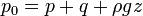
- where ρ is the density of the fluid, g is the local acceleration due to gravity, and z is the height above a datum.
- If the variation in height above the datum is zero, or so small it can be ignored, the above equation reduces to the following simplified form:

- In a mixture of ideal gases, total pressure refers to the sum of each gas' partial pressure.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.