Tocainide
 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
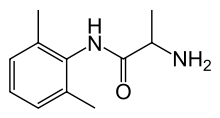
| N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)alaninamide | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601248 |
| Legal status | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 0.9-1 (oral) |
| Protein binding | 10-20% |
| Metabolism | glucuronidation (primary) |
| Half-life | 9-14 R, 13-20 S |
| Excretion | 30-50% urine (unchanged) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 41708-72-9 |
| ATC code | C01BB03 |
| PubChem | CID 38945 |
| DrugBank | DB01056 |
| ChemSpider | 35632 |
| UNII | 27DXO59SAN |
| KEGG | D06172 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:9611 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1762 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C11H16N2O |
| Mol. mass | 192.258 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Tocainide (Tonocard) is a class Ib antiarrhythmic agent. It is no longer sold in the United States.
Quick look at the Pharmacokinetics
Tocainide is a lidocaine analog, that does not have significant 1st pass metabolism. It is found in two enantiomers. The R isomer is 4x as potent as the S. Oral bioavailability is 0.9-1.0. In the blood tocainide is 10-20% protein bound. The Volume of distribution is 2.5-3.5 L/kg. 30-50% is excreted unchanged in the urine. The more active R-isomer is cleared faster in anephric patients or those with severe renal dysfunction. The main metabolite is the glucuronidated tocainide carbamic acid. The glucuronosyl transferase is apparently induced by rifampin. Weak inhibition of Cyp1A2 leads to a mild theophylline interaction. (Not verbatim)
External links
Burton ME. Applied Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics: Principles of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||