Thujopsene
| Thujopsene | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IUPAC name (1aS,4aS,8aS)-2,4a,8,8-Tetramethyl-1,1a,4,4a,5,6,7,8-octahydrocyclopropa[d]naphthalene | |
| Other names Sesquichamene; Thujopsen; Widdrene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 470-40-6 |
| PubChem | 442402 |
| ChemSpider | 390845 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C\2=C(\[C@H]3[C@@]1([C@](CCCC1(C)C)(C)C/2)C3)C|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C15H24 |
| Molar mass | 204.35 g mol−1 |
| Density | 0.936 g/mL (20 °C)[1] |
| Boiling point | 258-260 °C[1] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Thujopsene is a natural chemical compound, classified as a sesquiterpene, with the molecular formula C15H24.
Thujopsene is found in the essential oil of a variety of conifers,[2] in particular Juniperus cedrus in which it comprises around 2.2% of the weight of the heartwood.[3]
Biosynthesis
Thujopsene is biosynthesized from farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP):[4]
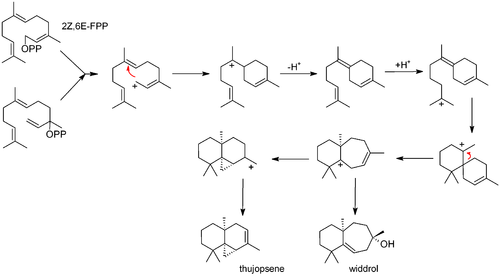
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "(−)-Thujopsene". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ Erdtman, H.; Norin, T. (1960). "Structure of thujopsene and hinokiic acid from coniferous wood". Chemistry and Industry (22): 622–623.
- ↑ Runeburg, Jarl; Gramstad, Thor; Larsson, Lennart; Dodson, R. M. (1960). "The Chemistry of the Natural Order Cupressales XXX. Constituents of Juniperus cedrus L.". Acta Chemica Scandinavica 14: 1991–1994. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.14-1991.
- ↑ J. Mann et al. Natural Products: their chemistry and biological significance. ISBN 978-0582060098.