Thionyl tetrafluoride
| Thionyl tetrafluoride | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
 |
 | |
| IUPAC name Thionyl tetrafluoride | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 13709-54-1 | |
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | SOF4 | |
| Appearance | colorless gas | |
| Density | 1.653-0.0036T (°C) liquid[1] | |
| Melting point | -99.6°C | |
| Boiling point | -49°C (5090 cal/mol heat of vapourisation[1]) | |
| Solubility in water | reaction in water | |
| log P | 7.2349-859.58/T-26275/T²[1] | |
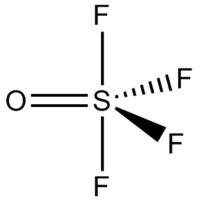
| Structure | ||
| Molecular shape | distorted trigonal bipyramid | |
| Hazards | ||
| R-phrases | R36/37/38[2] | |
| Related compounds | ||
| Related oxohalides | Thionyl fluoride Selenyl tetrafluoride | |
| Related compounds | Phosphoryl trifluoride pentafluorosulfur hypofluorite sulfuryl fluoride | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Thionyl tetrafluoride is an inorganic compound gas with the formula SOF4. It is also known as sulfur tetrafluoride oxide. The shape of the molecule is a distorted trigonal bipyramid. The oxygen is found on the equator. The atoms on the equator have shorter bond lengths than the fluorine atoms on the axis. The sulfur oxygen bond is 1.409Å. A S-F bond on the axis has length 1.596Å and the S-F bond on the equator has length 1.539Å. The angle between the equatorial fluorine atoms is 112.8°. The angle between axial fluorine and oxygen is 97.7°. The angle between oxygen and equatorial fluorine is 123.6° and between axial and equatorial fluorine is 85.7°.[3] The fluorine atoms only produce one NMR line, probably because they exchange positions.[1]
Formation
Thionyl fluoride reacting with fluorine gas can produce thionyl tetrafluoride.[1] This was how the gas was first discovered by Moissan and Lebeau in 1902. They identified the formula by the pressure changes resulting from the reaction. Silver fluoride and platinum are capable of catalyzing the reaction.
It can also be formed by heating sulfur hexafluoride with air to 400°.[4] This can happen when inhaling through a lit cigarette. Or the reaction of silver difluoride with thionyl fluoride at 200 degrees.[5] Another way to form it is by electrolyzing hydrogen fluoride with a solution of sulfur dioxide, which also made oxygen difluoride and sulfuryl fluoride.[6] Also thionyl chloride or thionyl fluoride electrolyzed with hydrogen fluoride produced even more of the gas.
Reactions
Thionyl tetrafluoride reacts with water to make hydrofluoric acid, sulfurofluoridic acid, and sulfuryl difluoride. Mercury can strip off fluoride to make thionyl fluoride and mercurous fluoride. Strong bases result in formation of fluoride and fluorosulfate ions.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Harry Julius Emeléus and A.G. Sharpe Advances in Inorganic Chemistry Volume 2 Academic Press 1960 page 117
- ↑ "Safety (MSDS) data for thionyl tetrafluoride". Oxford University. 2005-09-02. Retrieved 2008-07-29.
- ↑ Lise Hedberg and Kenneth Hedberg "Thionyl tetrafluoride. Reanalysis of the molecular structure and resolution of the multiple model problem" the Journal of Physical Chemistry March 1982 vol 86 page 598 doi 10.1021/j100394a004
- ↑ "SF6 Gas Properties".
- ↑ http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja01589a013
- ↑ Shunji Nagase Fluorination of Inorganic Sulfur Compounds Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan vol 42 page 2062 1968