Tetrathionate

The tetrathionate anion, S4O62−, is a sulfur oxoanion derived from the compound tetrathionic acid, H2S4O6. Two of the sulfur atoms present in the ion are in oxidation state 0 and two are in oxidation state +5. Alternatively, the compound can be viewed as the adduct resulting from the binding of the Lewis base S22− to SO3. Tetrathionate is one of the polythionates, a family of anions with the formula [Sn(SO3)2]2−.[1] Its IUPAC name is (sulfonatodisulfanyl)sulfonate, the name of its corresponding acid is (sulfodisulfanyl)sulfonic acid. The Chemical Abstracts Service identifies tetrathionate by the CAS Number 15536-54-6.
Formation
Tetrathionate is a product of the oxidation of thiosulfate, S2O32−, by iodine, I2:
- 2S2O32− + I2 → S4O62− + 2I−
Structure
Tetrathionate's structure can be visualized by following three edges of a cube, as in the diagram below. The structure shown is the configuration of S4O62− in BaS4O6·2H2O and Na2S4O6·2H2O. Dihedral S-S-S-S angles approaching 90° are common in polysulfides.
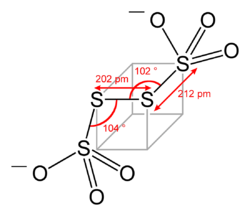
Compounds
Compounds containing the tetrathionate anion include sodium tetrathionate, Na2S4O6, potassium tetrathionate, K2S4O6, and barium tetrathionate dihydrate, BaS4O6·2H2O.
Properties
As other species of sulfur at intermediate oxidation state, such as thiosulfate, tetrathionate can be responsible for the pitting corrosion of carbon steel and stainless steel.
Tetrathionate has also been found to serve as a terminal electron acceptor for Salmonella Typhimurium, whereas existing thiosulfate in the lumen of mammals is oxidized by reactive oxygen species released by the immune system (mainly NADPH oxidase produced superoxide) to form tetrathionate. This aids in the growth of the bacterium, helped by the inflammatory response.[2]
See also
- Corrosion
- Dithionite
- Polysulfides
- Thiosulfate
References
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0080379419.
- ↑ Winter, Sebastian E. "Gut Inflammation Provides a Respiratory Electron Acceptor for Salmonella." Gut Inflammation Provides a Respiratory Electron Acceptor for Salmonella. Nature, 23 Sept. 2010. Web. 28 Mar. 2013.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tetrathionates. |