Tetrated dodecahedron
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Tetrated dodecahedron | |
|---|---|
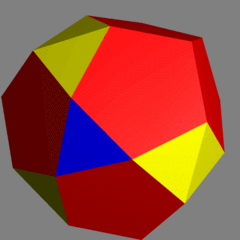 | |
| Type | near-miss Johnson solid |
| Faces | 4+12 triangles 12 pentagons |
| Edges | 54 |
| Vertices | 28 |
| Vertex configuration | 4 (5.5.5) 12 (3.5.3.5) 12 (3.3.5.5) |
| Symmetry group | Td |
| Properties | convex |
The tetrated dodecahedron is a near-miss Johnson solid. It was first discovered in 2002 by Alex Doskey. It was then independently rediscovered in 2003 and named by Robert Austin.[1]
It has 28 faces: twelve regular pentagons arranged in four panels of three pentagons each, four equilateral triangles (shown in blue), and six pairs of isosceles triangles (shown in yellow). All edges of the tetrated dodecahedron have the same length, except for the shared bases of these isosceles triangles, which are approximately 1.07 times as long as the other edges. This polyhedron has tetrahedral symmetry.
Net
The 12 pentagons and 16 triangles are colored in this net by their locations within the tetrahedral symmetry.

Related polyhedra
| Dodecahedron (Platonic solid) |
Icosidodecahedron (Archimedean solid) |
Pentagonal orthobirotunda (Johnson solid) |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
See also
Notes
| ||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.