Tetralone
| Tetralone[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IUPAC name 3,4-dihydro-2H-naphthalen-1-one | |
| Other names α-Tetralone; 1-Tetralone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 529-34-0 |
| PubChem | 10724 |
| ChemSpider | 10273 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C10H10O |
| Molar mass | 146.19 g mol−1 |
| Density | 1.099 g/mL |
| Melting point | 2–7 °C |
| Boiling point | 113–116 °C (6 mmHg) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Tetralone is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C10H10O. It is a common intermediate in organic synthesis. It is a ketone derivative of tetralin.
The Haworth reaction is a classic method for the synthesis of tetralone.[2][3] Benzene is reacted with succinic anhydride by a Friedel–Crafts acylation, the intermediate product is reduced and a second Friedel–Crafts acylation takes place upon the addition of acid.
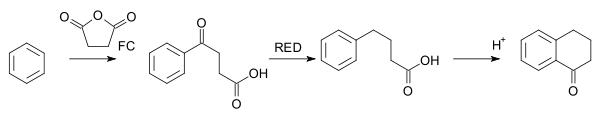 Haworth reaction
Haworth reaction
The structural isomer 2-tetralone is also known.
 Chemical structure of 2-tetralone
Chemical structure of 2-tetralone
References
- ↑ α-Tetralone at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Robert Downs Haworth (1932). "Syntheses of alkylphenanthrenes. Part I. 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-Methylphenanthrenes". J. Chem. Soc.: 1125. doi:10.1039/JR9320001125.
- ↑ Name Reactions: A Collection of Detailed Reaction Mechanisms By Jie Jack Li Published 2003 Springer ISBN 3-540-40203-9